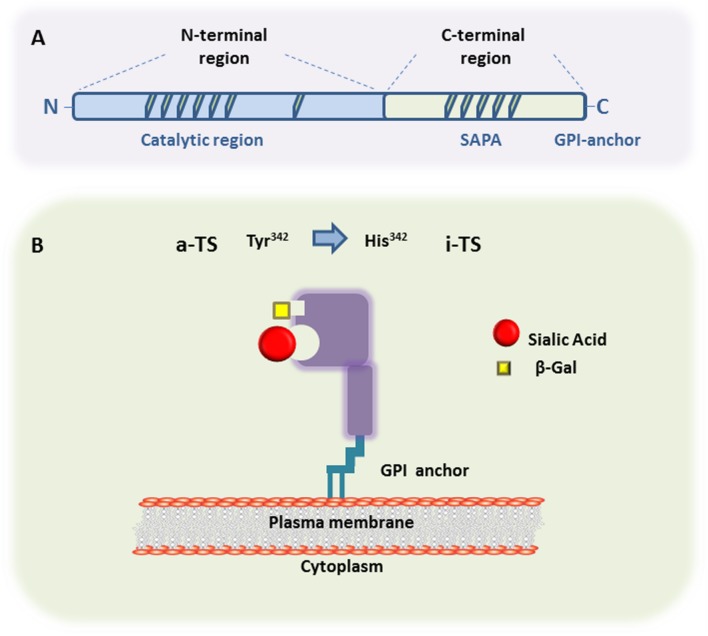
FIGURE 1.
Trans-sialidase structure. (A) Representative scheme of the primary structure of metacyclic- and a bloodstream trypomastigote-TS members belonging to either Group I (active-TS) or Group II (inactive-TS), showing the N-terminal and C-terminal domains. (B) Representative 3D structure of active (a-TS) and inactive (i-TS) forms of Trypanosoma cruzi-TS. T. cruzi-TS proteins are bound to the parasite surface through GPI-anchors. Active-TS sialylates parasite’s mucin-like molecules, as well as host cell surface glycoconjugates. Inactive-TS in turn acts as a parasite adhesin and it is differentiated from a-TS by a single mutation in the catalytic residue of Tyrosine at the position 342, which is commonly changed by a Histidine.