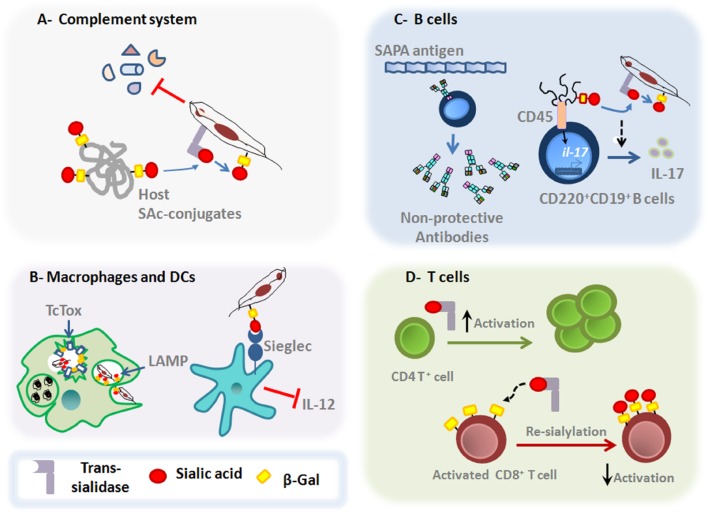
FIGURE 2.
Main roles of T. cruzi TS on the host immune responses. (A) Upon entry in the host milieu, which is rich in SAcs donors, the parasite surface gets a negatively charged barrier due to a reaction catalyzed by TS, conferring protection against the complement-mediated killing. (B) TS favors T. cruzi escape from the parasitophorous vacuole, process in which LAMP and Tc-Tox proteins are also shown to be involved. Moreover, TS is able to interfere with IL-12 secretion by dendritic cells through the interaction between sialylated molecules on T. cruzi surface and Siglecs on dendritic cell surface. (C) SAPA-antigen induces the production of non-protective antibodies. Moreover, recent findings have show that TS acts on both mature follicular and marginal zone CD220+CD19+B cells to induce the expression of IL-17 by a non-canonical signaling pathway. These signaling events promote changes in the glycosylation profile of CD45 that result in their phosphatase activity and subsequent activation of downstream signals leading to the Il-17 gene expression. (D) TS can also induce the activation of CD4+T cells in vivo. In addition, TS can also promote changes in the sialylation pattern of activated CD8 +T cells, dampening the protective functions of MHC class I-dependent lymphocyte killing responses against T. cruzi parasites.