Figure 3.
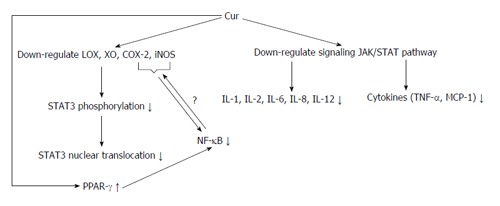
Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin in vivo. Curcumin (Cur) down-regulates some of the factors involved in inflammation, inhibiting NF-κB activation and causing its anti-inflammatory effects. Also, Cur with increasing PPAR-γ expression directly inhibits NF-κB activation. NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; TNF: Tumor necrosis factors; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IL: Interleukins; LOX: Lipoxygenase; COX: Cyclooxygenase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; XO: Xanthine oxidase.
