Figure 3.
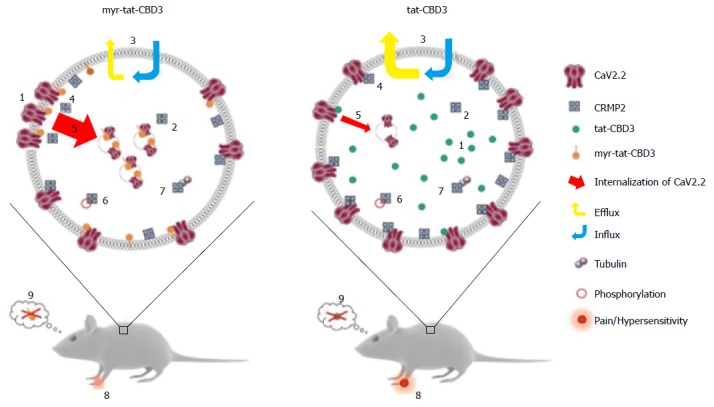
A possible model for N-myristoylated collapsin response mediator protein 2 peptide’s actions on CaV2.2 trafficking and efficacy in neuropathic pain model. Application of an N-myristoylated tat-conjugated CRMP2 peptide (myr-tat-CBD3) results in membrane-delimited “rimming” of the peptide whereas the non-myristoylated version (tat-CBD3) appears to be spatially diffusely distributed in the cell cytoplasm. Analysis of penetration of peptides into GPMVs, which are “blebs” of membrane devoid of organelles and actin cytoskeleton, reveals an unrestricted distribution of the membrane sensitive dye (di-4-ANNEPDHQ) with tat-CBD3, whereas the myristoylated peptide induces a lateral heterogeneity of the fluorescent signal resulting in dye aggregation into micro domains within these model membranes[122]. While CRMP2 has been demonstrated to exist as a tetramer, the oligomeric state of membrane proximal CRMP2 is as yet unknown; however, neither peptide appears to affect CRMP2 oligomerization[123]. Whereas the cells take up both forms of the peptide with similar efficiency, the myristoylated peptide demonstrates a lesser degree of efflux[124]. The apparent increase in retention of myr-tat-CBD3 translates into a superior potency and efficacy in inhibition of evoked calcium influx in sensory neurons presumably via greater uncoupling of CRMP2-CaV2.2 interactions at or juxta-membrane[125]. Increased inhibition of CaV2.2 surface trafficking induced by myr-tat-CBD3 compared with tat-CBD3 may account[126] for the more pronounced restriction of calcium influx imposed by the myristoylated peptide. Cdk5-phosphorylated CRMP2 has been demonstrated to have an enhanced interaction with CaV2.2[129]; however myr-tat-CBD3 does not affect the levels of Cdk5-phosphorylated CRMP2[127], thereby ruling out a role of phosphorylated CRMP2 in regulating calcium influx. CRMP2 binding to tubulin is strengthened by the peptides[130]; the consequences of this are currently unknown. Importantly, where tat-CBD3 is completely ineffective in reversing mechanical hypersensitivity in a rat neuropathic pain model (tibial nerve injury), the myristoylated peptide reverses this hypersensitivity when administered in vivo[122]. Neither peptide elicits any reward-like addictive behaviors. GPMVs: Giant plasma membrane vesicles; CRMP: Collapsin response mediator proteins.
