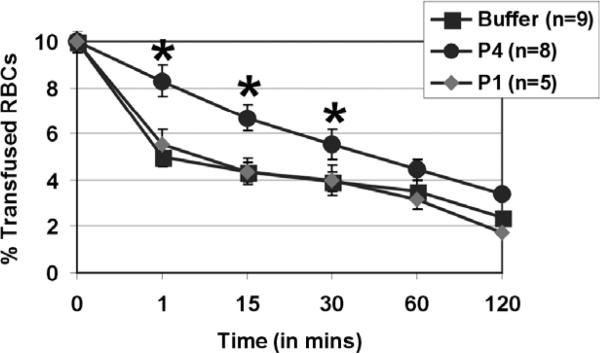
Fig. 4.
A CR1-derived 34-mer peptide prolongs the survival of transfused RBC in vivo. Fluorescently-labeled human group O RBCs equivalent to 10% of total mouse blood volume were injected intravenously into C57Bl/6 mice without (buffer, black squares, n = 9) or with peptide 1 (P1, grey diamond, n = 5) or peptide 4 (P4, black circles, n = 8) both given at 0.6 mM. At times indicated, venous blood was sampled and analyzed by flow cytometry for fraction of fluorescent RBCs. To show the clearance kinetics, injected RBCs at time 0 were taken as 10% and the remaining RBCs were calculated at different time points as the average for each group of mice with error bars depicting SEM. *p < 0.05 as compared to buffer treatment.