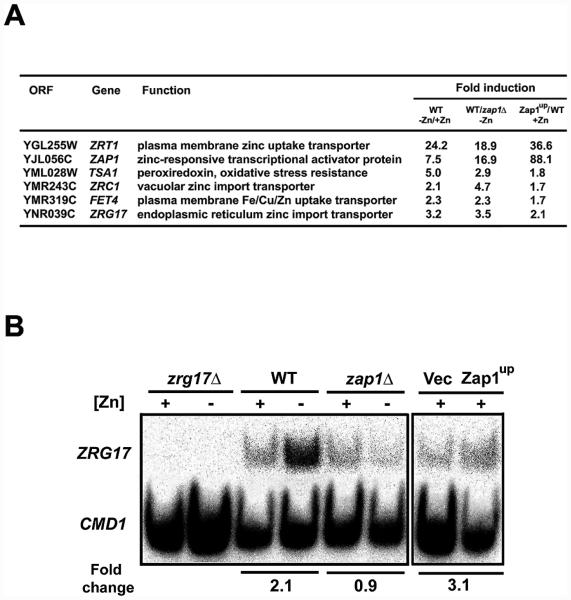
Figure 1. S1 nuclease protection assays confirm microarray results.
A) Previous microarray results for ZRG17 and select previously confirmed Zap1 target genes [11, 12]. B) ZRG17 mRNA levels were analyzed by S1 nuclease protection assays. Total RNA was isolated from cells grown under the same conditions as the microarray experiments. zrg17Δ mutant cells, wild-type cells (DY1457), or zap1Δ mutant cells (ZHY6) were grown in low zinc medium (LZM) supplemented with high zinc (+, 1000 μM ZnCl2) or low zinc (−, 1 μM ZnCl2) (left panel). LZM contains 1 mM EDTA and 20 mM citrate to buffer available zinc levels. Also, wild-type (DY1457) cells expressing either the vector (pYef2) or a Zap1up plasmid (pAFH35) were grown in zinc-replete SD medium containing 1 μM ZnCl2 and 2% galactose as the carbon source to drive expression of the constitutively active Zap1up allele from the GAL1 promoter (right panel). CMD1, encoding calmodulin, was used as a loading control. The fold changes shown were quantified from the level of ZRG17 mRNA normalized to CMD1 in each lane. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments.