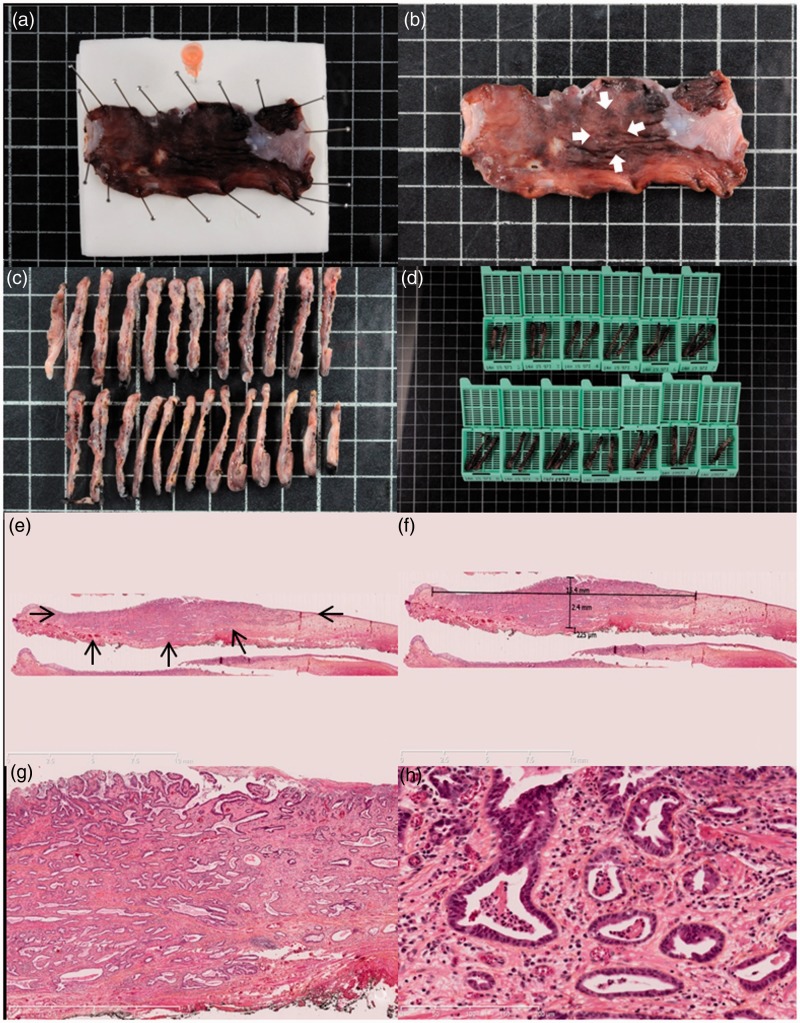
Figure 2.
Histopathological assessment of early Barrett’s carcinoma resected by endoscopic submucosal dissection. (a) Macroscopic view of the resected specimen after 24 hours of formaldehyde fixation, pinned to the polystyrene board with an orange needle to mark the oral side of the resection. (b) Macroscopic view of the resected specimen after fixation. Arrowheads show the 15 mm suspicious nodular lesion. (c) and (d) Processing of the specimen in 2–3 mm sections further included in paraffin blocks. (e) Histological view of the resected specimen showing an invasive adenocarcinoma (arrowheads) with submucosal infiltration and R0 margins, hematoxylin-eosin-saffron, 5×. (f) After digitization of the slide, measurement shows a submucosal invasion of 225 µm, making the lesion a pT1a sm1 lesion, with curative endoscopic treatment. (g) and (h) Histological view of the resected specimen at higher magnifications, Histological view of the resected specimen showing a well-differentiated tubulous adenocarcinoma with submucosal infiltration and R0 margins, and no vascular or lymphatic invasion, hematoxylin-eosin-saffron, 25× and 200×, respectively.