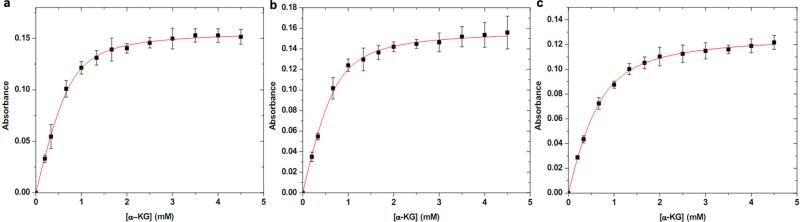
Extended Data Figure 1. Characterization of FtmOx1–α-KG complex.
a, Wild-type FtmOx1 and α -KG binding curve. The increase in absorbance at 520 nm as a function of α -KG concentration when it was added to a solution of wild-type FtmOx1 (0.9 mM) and FeII (0.72 mM) is plotted. On the basis of the equations described in the Methods (determining the α -KG dissociation constant), the Kd for wild-type FtmOx1 and α -KG is ~ 185 ± 35 μ M. b, Y224F-substituted FtmOx1 and α -KG binding curve. The increase of absorbance at 520 nm as a function of α -KG concentration when it was added to a solution of Y224F-substituted FtmOx1 (0.9 mM) and FeII (0.7 mM) is plotted. Kd for Y224F-substituted FtmOx1 and α -KG is ~ 198 ± 58 μ M. c, Y224A-substituted FtmOx1 and α -KG binding curve. The increase of absorbance at 520 nm as a function of α -KG concentration when it was added to a solution of Y224A-substituted FtmOx1 (0.7 mM) and FeII (0.51 mM) is plotted. Kd for Y224A-substituted FtmOx1 and α -KG is 204 ± 43 μ M. In a–c, the Kd was calculated based on the concentration of iron-loaded FtmOx1. The experiments were replicated three times and error bars represent s.e.m.