Figure 6.
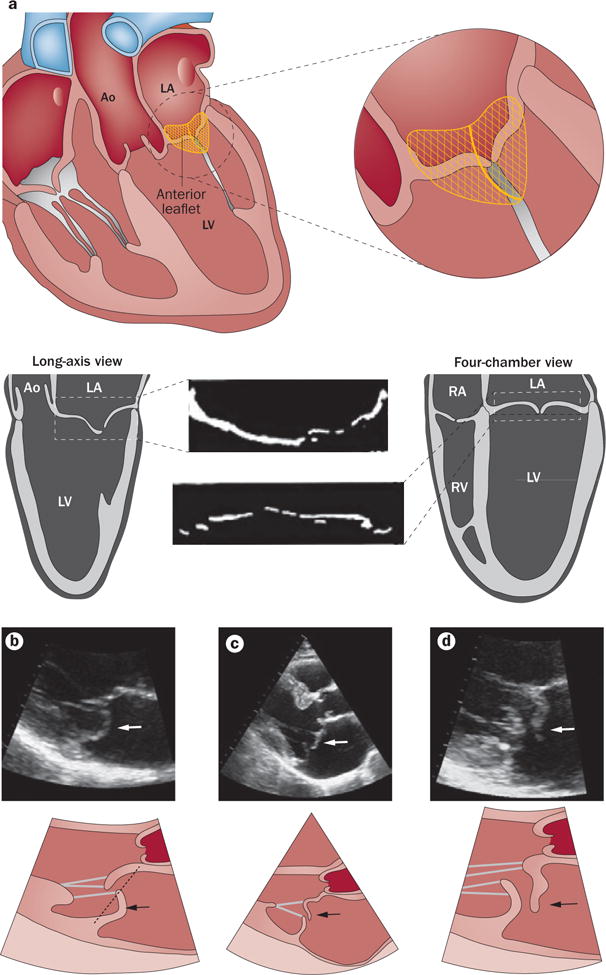
Echocardiographic diagnosis of mitral valve prolapse. a | Diagnosis of mitral valve prolapse must take into account the normal saddle shape of the valve and annulus, which produces opposite leaflet–annular relationships in perpendicular views. Mitral valve prolapse is most specifically diagnosed by leaflet displacement above the annular high points, imaged in long-axis views; and by leaflet misalignment at their point of coaptation. b | Parasternal long-axis echocardiographic view of posterior leaflet prolapse (arrows) beyond the annular hinge points (dashed line). c | Anterior leaflet prolapse and partial flail (partial eversion of the leaflet tip into the dilated LA; arrows) relative to the posterior leaflet, which is restricted, tethered by the dilated LV.90 These opposite leaflet displacements increase the regurgitant gap between the leaflets. d | Patient with extensive leaflet thickening and anterior leaflet flail (arrows). Abbreviations: Ao, aorta; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
