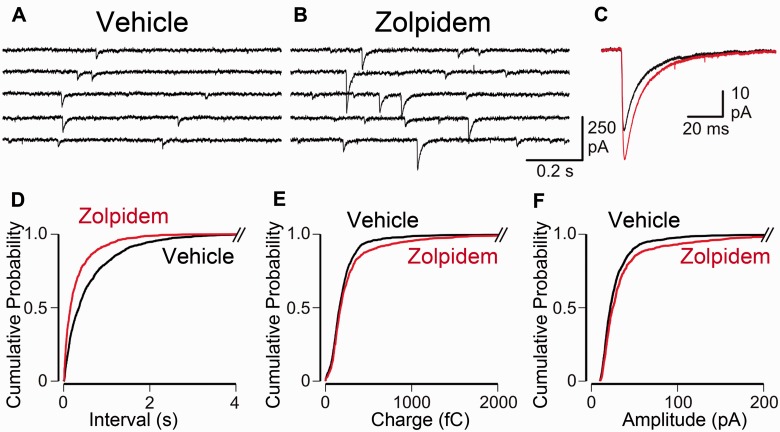
Figure 5.
Zolpidem treatment enhances postsynaptic inhibitory currents in layer 5 pyramidal neurons. (A and B) Spontaneous IPSC recordings from representative layer 5 pyramidal neurons from stroke-injured mice treated with (A) vehicle and (B) zolpidem. (C) Ensemble-averaged spontaneous IPSCs from the same pyramidal cells (vehicle, black; zolpidem, red), plotted on the same timescale. (D–F) Cumulative probability histograms of isolated events from seven stroke-injured vehicle-treated mice (n = 1300 events, 13 cells, 100 events per cell) and six stroke-injured zolpidem-treated mice (n = 800 events, eight cells, 100 events per cell) demonstrate differences in frequency, charge and amplitude of the events (Frequency, P = 10−24; Charge, P = 10−6; Amplitude, P = 10−8; Kolmogoroff-Smirnoff test).