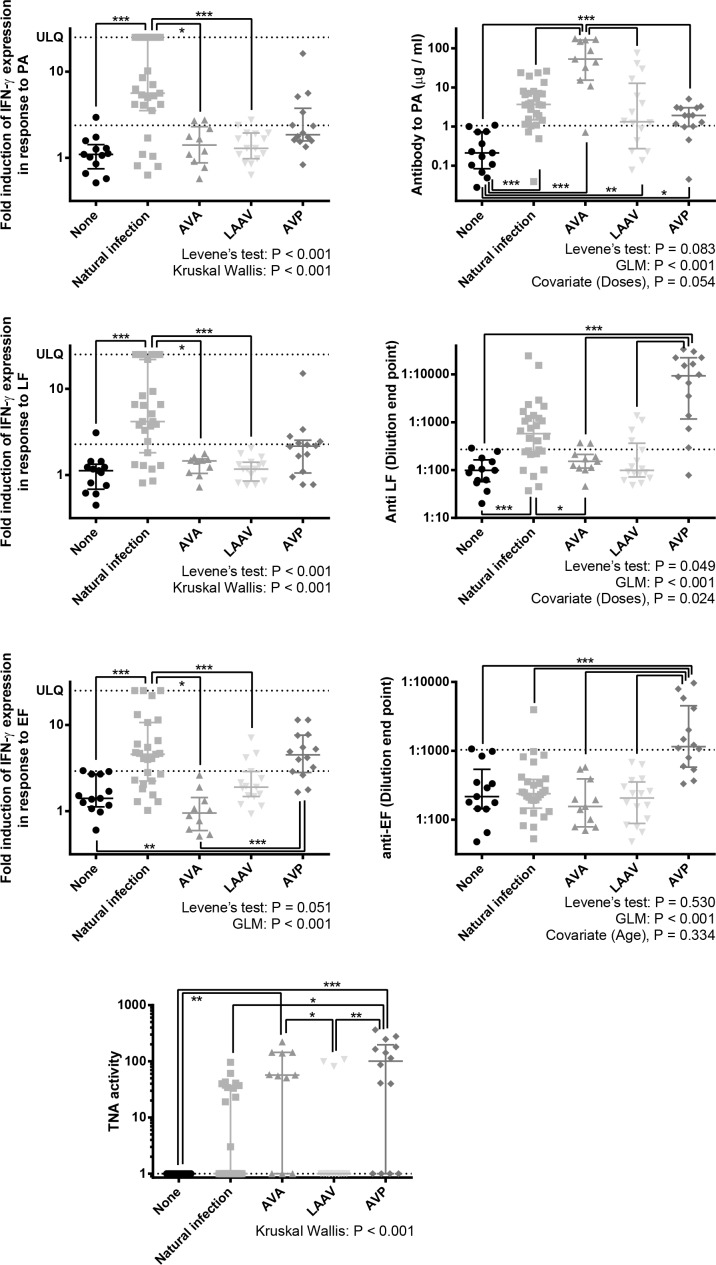
Fig 3. The memory immune responses towards parts of the Anthrax toxin systems in individuals who had suffered from cutaneous anthrax previously, been vaccinated against anthrax with either AVA, LAAV or AVP, or have no history of exposure to anthrax antigens.
Antibody responses were measured by ELISA, estimating antigen specific antibody in μg / ml or a dilution end point. IFN-γ T cell responses were estimated by ELISPOT and numerated as fold induction in IFN-γ producing cells by exposure to anthrax antigen, when compared to unstimulated cells. Toxin neutralisation was measured in the ED50 of cells exposed to anthrax toxin in the presence of the serum. ULQ signifies the upper limit of quantification, due to confluence of spots on the ELISPOT plate, which was regarded as 25 fold. An additional line has been included which is indicative of the 90 percentile of the naïve group. The purpose of this is to give an approximate indication of the number of individuals with greater than background antigen recognition. Statistical analysis is shown. First, Levene’s tests of unequal variances were performed to establish suitability for parametric analysis. Unsuitability necessitated Kruskal-Wallis tests with Dunn’s post-tests. Suitability allowed for GLM analysis which included any potential covariates suggested previously, with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons. The significance markers show results post-test comparisons: *** = P < 0.001, ** = P <0.01 * = P <0.05.