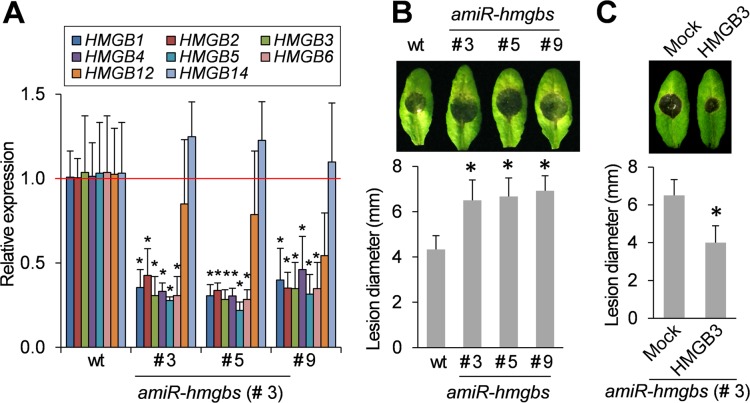
Fig 4. Silencing HMGBs increases susceptibility to B. cinerea.
A. Relative expression of HMGBs (HMGB1-HMGB14) in 4-week-old plant from three different amiR-hmgbs lines (#3, #5 and #9) was compared to their expression levels in wt plants, which was set at 1 and denoted by a red line. Data are the mean ± SD (n = 4). B. amiR-hmgbs lines showed enhanced susceptibility to B. cinerea infection. Representative disease symptoms at 3 dpi are shown in the upper panel, and the data corresponding to this time point are presented in the lower panel as the mean ± SD (n = 6). C. Extracellular HMGB3 restored resistance of amiR-hmgbs transgenic plants (line # 3) to B. cinerea. Leaves were infiltrated with water containing 1 μM HMGB3 one day before B. cinerea infection. Representative disease symptoms at 3 dpi are shown in the upper panel. Data corresponding to this time point are presented as the mean ± SD (lower panel, n = 6). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the untransformed wt plants in A and B or mock-treated amiR-hmgbs transgenic plants in C (t test, P < 0.05).