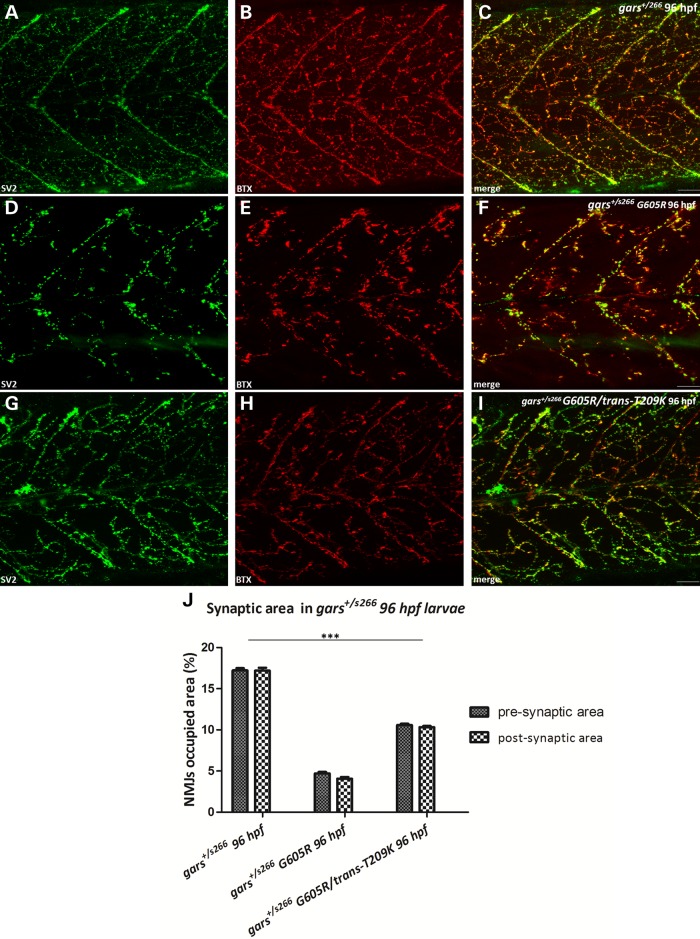
Figure 7.
Dominant toxicity is associated with dimerization. (A–I) Projections of confocal z-stacks at the level of hindgut extension (C: 42,57 μm; F: 42,3 μm; I: 31,22 μm) of gars+/s266, gars+/s266 G605R, gars+/s266 G605R/trans-T209K larvae at 96 hpf. (A–C) gars+/s266 uninjected larvae. (D–F) gars+/s266 larvae injected with G605R mRNA (n = 228 injected larvae, 33% of injected larvae gave a s266 phenotype). The expression of G605R caused a dramatic reduction of the pre- and post-synaptic densities in the injected larvae. (G–I) gars+/s266 larvae injected with G605R/trans-T209K mRNA (n = 153 injected larvae). However, trans-expression of T209K mutation ameliorated the observed NMJ phenotype probably due to lower levels of G605R Gars available for dimerization with wild-type Gars. (J) Quantification of synapse density in injected larvae (gars+/s266 n = 11 larvae, gars+/s266 G605R n = 15 larvae, gars+/s266 G605R/trans-T209K n = 19 larvae, ***P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA). Scale bars: 50 μm.