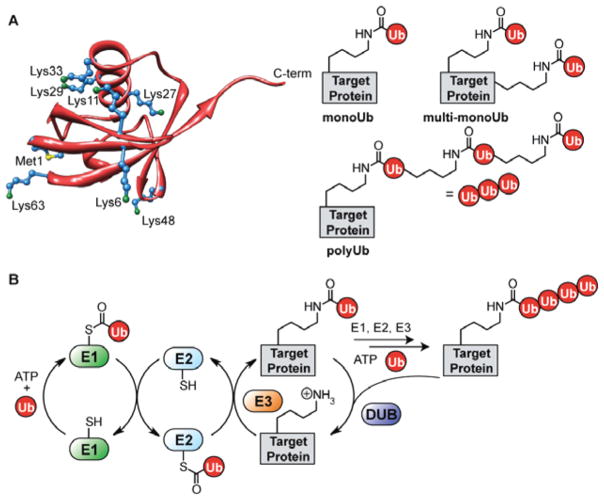
Figure 1.
The many facets of protein ubiquitination. (A) The structure of Ub (PDB code 1UBQ118) showing all seven lysines (blue, with green nitrogen atom) and the N-terminal methionine (blue, with yellow sulfur atom). Also, each of the different types of Ub modifications are shown: monoUb (where a single lysine of the target is modified), multi-monoUb (where multiple lysines in the target are modified), and polyUb (where one of the eight amino groups in Ub serves as the point of attachment for a growing polymer chain). (B) The enzymatic cascade leading to Ub conjugation and removal: E1 activating, E2 conjugating, E3 ligase, and deubiquitinating (DUB) enzymes.