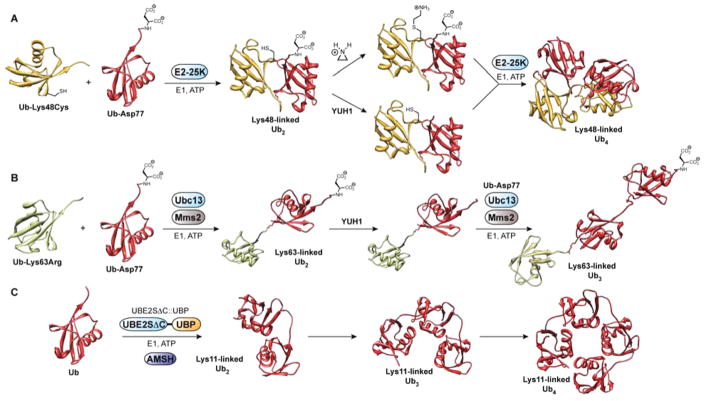
Figure 3.
Controlled synthesis of Lys48-, Lys63-, and Lys11-linked polyUb chains. (A) Enzymatic synthesis of Lys48-linked polyUb chains using Lys48-linkage specific E2 conjugating enzyme E2–25K. In the final step leading to Lys48-linked Ub4, two different Lys48-linked Ub dimers are required: one with a C-terminal aspartate cap and thiolysine residue at Lys48, and another with a free C-terminal Gly76 and Lys48 blocked with cysteine. The dimers are coupled through the thiolysine and free C-terminus. The proximal Ub (i.e., the only monomer not tethered to another Ub molecule) has an Asp77 cap, while the distal Ub (i.e., the last Ub in the tetramer) contains a Lys48Cys mutation. YUH1: yeast Ub hydrolase 1. PDB code: 2O6V.47 (B) Enzymatic synthesis of Lys63-linked polyUb chains using heterodimeric Lys63-linkage specific E2 conjugating system Ubc13/ Mms2. The proximal Ub has an Asp77 cap, while the distal Ub (shown in green) contains a Lys63Arg mutation. PDB code: 3HM3.119 (C) Enzymatic synthesis of Lys11-linked polyUb chains using an engineered Lys11-linkage specific E2 conjugating enzyme UBE2SΔC::UBP. Using UBE2SΔC::UBP alone leads to a mixture of Lys11- and Lys63-linked chains, thus AMSH is added to cleave all Lys63-linkages and obtain a homogeneous product. Dimers, trimers, and tetramers are produced in the same reaction. AMSH: associated molecule with the SH3 domain of STAM. PDB code: 2XEW.55