Figure 3.
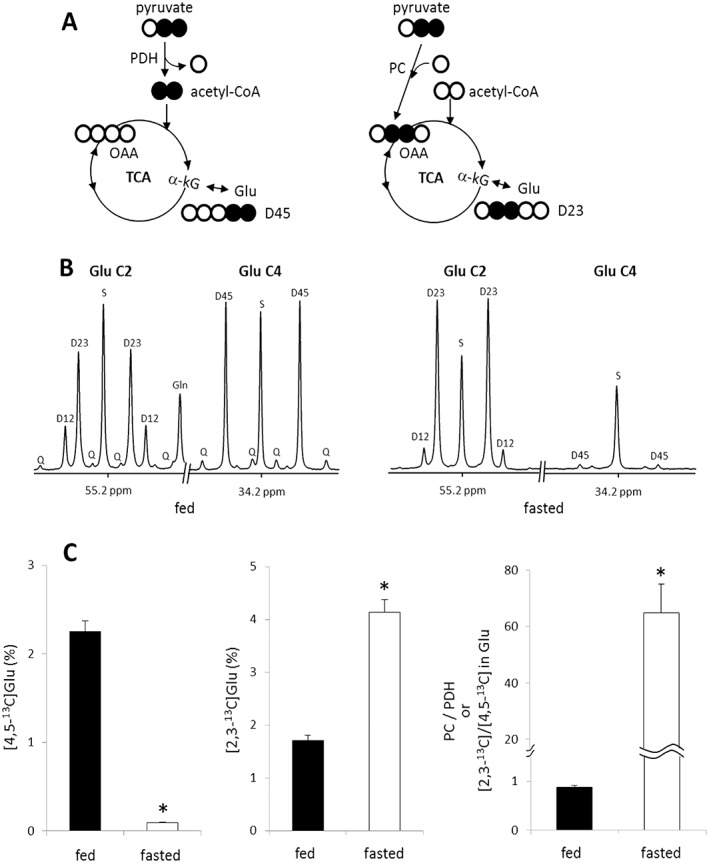
Detection of pyruvate entry to the TCA cycle through PC or PDH Based on NMR Analysis of Hepatic Glutamate in Rats Given [2,3‐13C]pyruvate. The entry of [2,3‐13C]pyruvate to the TCA cycle through PDH yields [4,5‐13C]glutamate while the entry through PC produces [2,3‐13C]glutamate after the condensation of [2,3‐13C]oxaloacetate and acetyl‐CoA followed by the forward turn through the TCA cycle (A). In 13C NMR spectra of C2 and C4 regions of glutamate isolated from liver, the signal from [4,5‐13C]glutamate is very strong in fed animals, but negligible in fasted rats. The signal from [2,3‐13C]glutamate is strong in fed animals and very strong in fasted animals (B). The fraction of D45 ([4,5‐13C]glutamate) was measured by assuming the singlet at C4 ([4‐13C]glutamate) as natural abundance 13C, and it was 2.25% in fed animals and only 0.09% in fasted animals. Likewise, the fraction of D23 ([2,3‐13C]glutamate) was 1.70% in fed animals and 4.13% in fasted animals. The ratio of [2,3‐13C]/[4,5‐13C] in glutamate, reflecting the ratio of anaplerosis/PDH, was dramatically higher in fasted rats compared with fed rats (D). Other small resonances in the spectra are from glutamate isotopomers produced through extensive turnover of the TCA cycle. D12, doublet from coupling of C1 with C2; D23, doublet from coupling of C2 with C3; D34, doublet from coupling of C3 with C4; Q, doublet of doublets, or quartet, arising from coupling of C2 with both C1 and C3 or from coupling of C4 with both C3 and C5; D45, doublet from coupling of C4 with C5; S, singlet; *, P < 0.001. n = 6–7 in each group.
