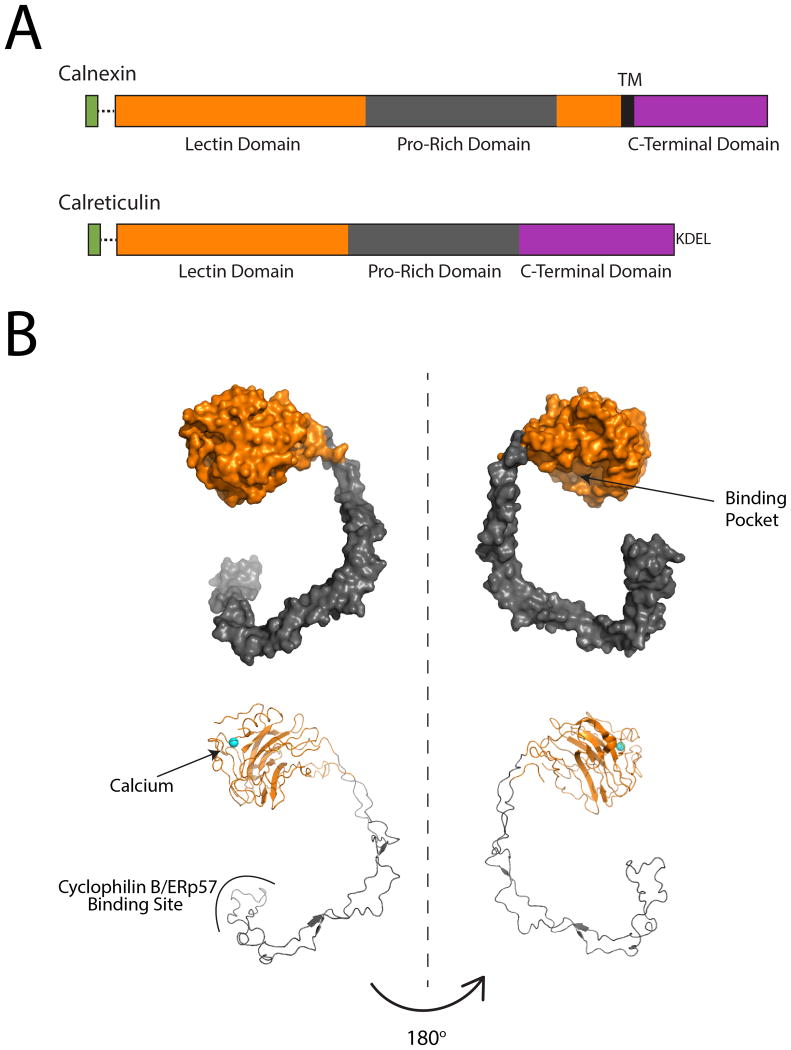
Figure 2. Structural and domain organization of calnexin and calreticulin.
A. Linear cartoon representations of calnexin and calreticulin. Both proteins possess a cleavable ER-targeting N-terminal signal sequence (green), a lectin domain (orange) and a C-terminal domain (purple). Calnexin possesses a single-pass transmembrane domain (black) that couples calnexin to the ER membrane and supports a cytoplasmic C-terminal domain. Calreticulin is soluble protein that is retained in the ER through its C-terminal KDEL sequence. B. Surface and ribbon representations of the crystal structure of the calnexin luminal domain (PDB: 1JHN)(40). The globular lectin domain (orange) forms a binding pocket to accommodate monoglucosylated clients and contains a calcium-binding site, with a single Ca2+ ion shown in cyan. The P-domain (gray) protrudes from the globular domain into a hook-like shape. Cyclophilin B and ERp57 bind at the tip of the P-domain.