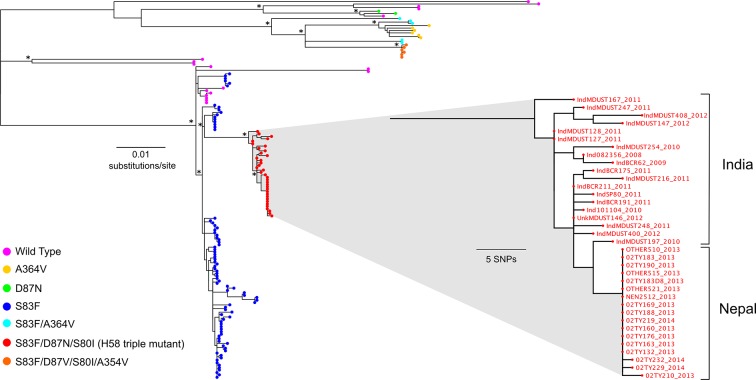
Figure 4. The phylogenetic structure of fluoroquinolone resistant Salmonella Typhi in a regional context.
Maximum likelihood phylogeny based on core-genome SNPs of 136 (78 from the RCT) Salmonella Typhi isolates from Nepal and neighbouring India (Supplementary file 1). Main tree shows the overall phylogenetic structure and the presence of specific combinations of mutations in gyrA (S83F, D87V and D87N), parC (S80I) and parE (A364V). The inset shows a magnified view of the fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella Typhi H58 triple mutants from Nepal and their close association with similarly fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella Typhi H58 triple mutants from India (Wong et al., 2015). The scale bar on the primary tree indicates the number of substitutions per variable site, while that in the inset indicates genetic distance in number of SNPs (see methods). Asterisks indicate ≥85% bootstrap support at nodes of interest.