Figure 1.
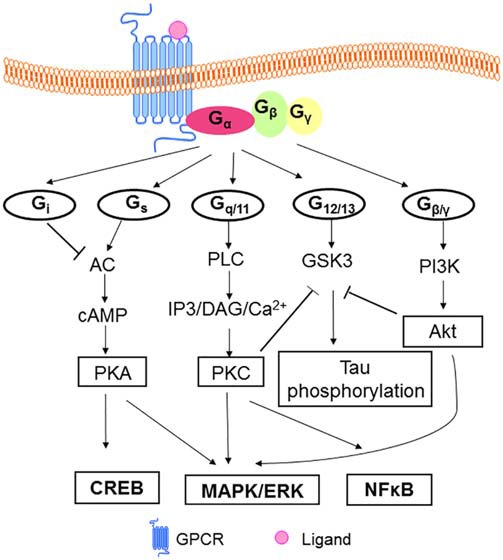
Model of GPCRs mediated signaling pathways. In classical model, heterotrimeric G proteins (α, β, γ subunits) mediate signal transduction via the receptor. Signal transduction initiated when ligands bind to GPCRs. The resulting conformation change promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP on the Galpha subunit of G proteins. Gs activates AC leading to the production of cAMP in cells, then cAMP binds to the regulatory subunit of PKA, regulating the phosphorylation of the GPCR and leading the process of desensitization of GPCR. PKA can regulate the level of CREB (Zeitlin et al., 2011) and mediates MAPK ERK pathway (New and Wong, 2007). Gq/11 controls the activity of PLC, which hydrolyzes PIP2 to generate IP3 and DAG. IP3 and DAG in turn lead to an increase in the intracellular concentrations of free Ca2+, regulation of NFκB (Arendash et al., 2009) and the activation of a number of protein kinases and pathways, including PKC/MAPK/ERK (Ritter and Hall, 2009). GPCR activate PI3K/Akt cascades through Gβγ (New and Wong, 2007). Gi inhibits AC, and G12/13 is suggested to activate GSK3 in neuronal cells (Sayas et al., 2002a,b). GSK3 is involved in tau phosphorylation with regard to AD pathology (Ly et al., 2013). And Akt and PKC can inhibit GSK3 activity (New and Wong, 2007; Langmead et al., 2008). Abbreviations: GPCR(s), G protein-coupled receptor(s); GDP, guanosine diphosphate; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; AC, adenyl cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PLC, phospholipase C; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate; IP3, inositol triphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PKC, protein kinase C; PI3K, phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase-3; AD, Alzheimer’s Disease.
