Fig. 4.
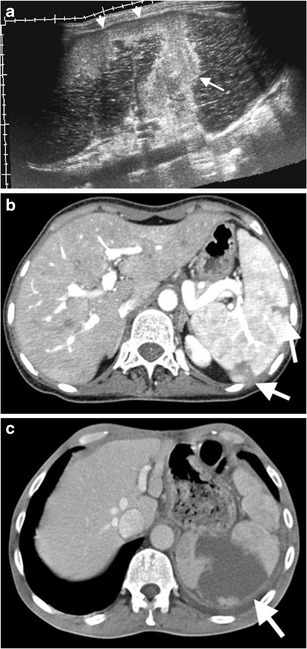
Splenic infarcts with various clinical conditions. (a) Panoramic view of gray scale US of a 54-year-old man with atrial fibrillation demonstrates hyperechoic infarct (arrow) traversing splenic parenchyma from the hilum to a peripheral part of the spleen. Neighbouring subcapsular portion of the spleen exhibits a hyperechoic appearance (arrowheads) representing subcapsular infarct. (b) Axial contrast-enhanced CT of a 21-year-old woman with polyarteritis nodosa reveals peripheral wedge-shaped low attenuated infarcts (arrows). (c) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image of a 79-year-old man with atrial fibrillation reveals a peripheral wedge-shaped low attenuated infarct (arrow)
