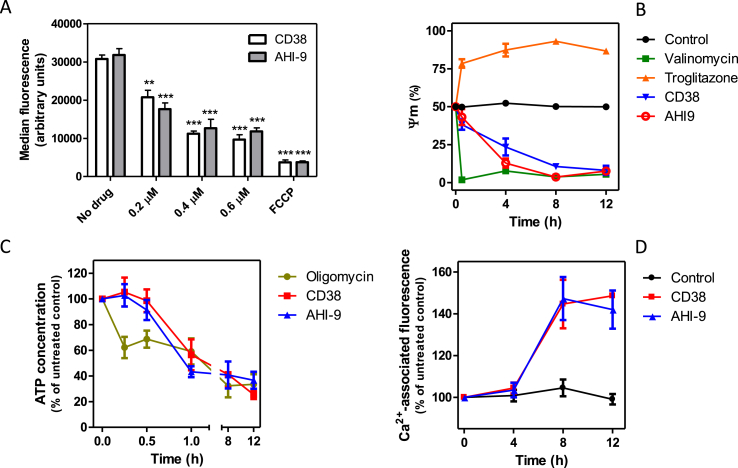
Fig. 4.
Effects of bisphosphonium compounds on mitochondrial functionality in live BF trypanosomes. (A) Dose-dependency of effect of CD38 and AHI-9 on mitochondrial membrane potential Ψm after four hours of exposure, measured by flow cytometry using the indicator fluorophore TMRE. Data are the triplicate and SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired Student's t-test: **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (B) Effects of 0.7 μM CD38 and AHI-9 on Ψm over a period of 8 h, using 0.1 μM valinomycin and 10 μM troglitazone as controls for membrane depolarisation and hyperpolarisation, respectively. Data are the triplicate and SEM of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences were observed for CD38 (P < 0.05, 30 min; P < 0.01, 4 h; P < 0.001, 8 and 12 h) and for AHI-9 (P < 0.001 for 4, 8 and 12 h). (C) The effects of 0.7 μM CD38 or AHI-9 on the total cellular ATP content. Oligomycin (2 μg/mL) was used as positive control and was significantly different from untreated controls at all time points (P < 0.01) whereas the bisphosphonium compounds only induced significantly reduced ATP levels at 60 min (P < 0.01). All data are the average and SEM of 3–4 independent experiments. (D) Assessment of intracellular calcium levels using the Fluo-8 indicator dye. Data are presented as percentage of the fluorescence level at time = 0 h for the untreated control cells. Fluorescence was significantly increased after treatment with 0.7 μM CD38 (P < 0.05, 8 h; P < 0.01, 12 h) or AHI-9 ((P < 0.05, 8 and 12 h). Average and SEM of three independent experiments.