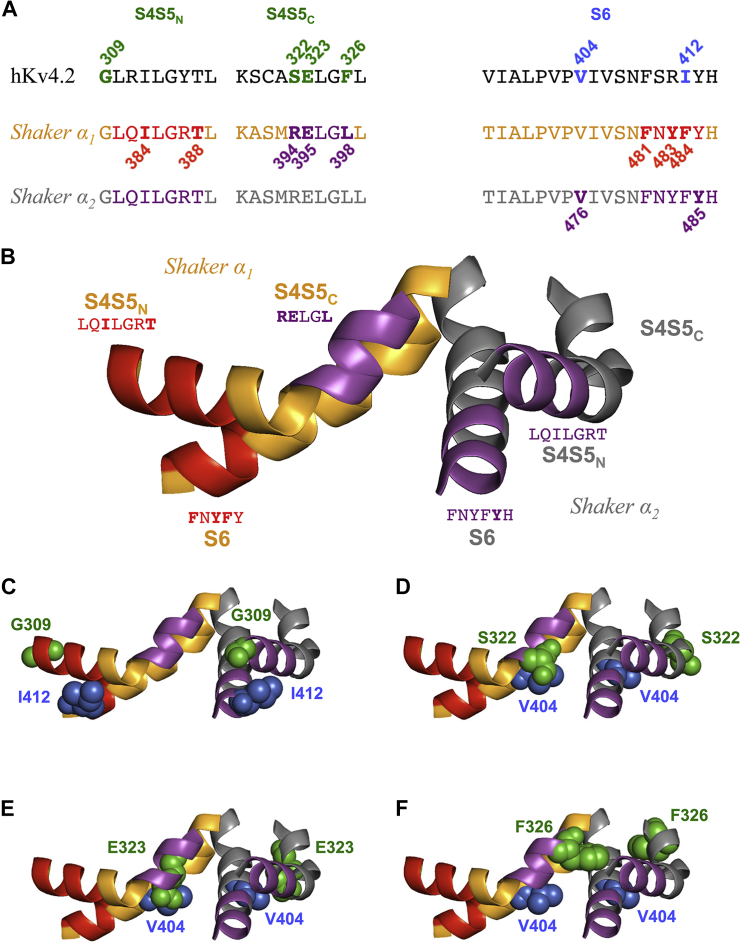
Figure 11.
S4S5 and S6 domains and amino acids involved in electromechanical coupling in Kv4.2 and Shaker channels. (A) The previously studied S4S5N, S4S5C, and S6 domains in human Kv4.2 (16) are aligned with the corresponding Shaker domains (Shaker α1 (orange) and Shaker α2 (gray) represent two neighboring α-subunits). The numbered Kv4.2 residues in S4S5 (green) and S6 (blue) were tested for intra- and/or intersubunit interactions in this study. In Shaker, the S4S5N residues I384 and T388 are thought to insert into a hydrophobic pocket formed by the S6 residues F481, Y483, and F484 of the same α-subunit (22). The S4S5C residues R394, E395, and L398 of Shaker α1, and the S6 residue Y485 of Shaker α2 are involved in the RELY intersubunit interaction under the control of V476 (23). (B) S4S5 and S6 of two neighboring α-subunits in the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera crystal structure (19) illustrate putative intra- and intersubunit interactions in the Shaker channel. Domains involved in intrasubunit interactions between S4S5N and S6 in Shaker α1 are shown in red. The S6 domain of Shaker α2 is nestled between S4S5N of Shaker α2 (intrasubunit interaction) and S4S5C of Shaker α1 (intersubunit interaction, magenta). Amino acid sequences and color coding correspond to (A). (C–F) Homology modeling of the Kv4.2 S4S5 (green) and S6 (blue) residues tested for intra- and/or intersubunit interactions in this study. The relevant portions of two neighboring α-subunits are shown, and the ribbon representation is colored according to (B). Kv4.2 coupling pairs: G309/I412 (C), S322/V404 (D), E323/V404 (E), and F326/V404 (F). The Kv4.2 residues are modeled on both α-subunits. They are shown in space-filling representation and the color coding corresponds to (A).