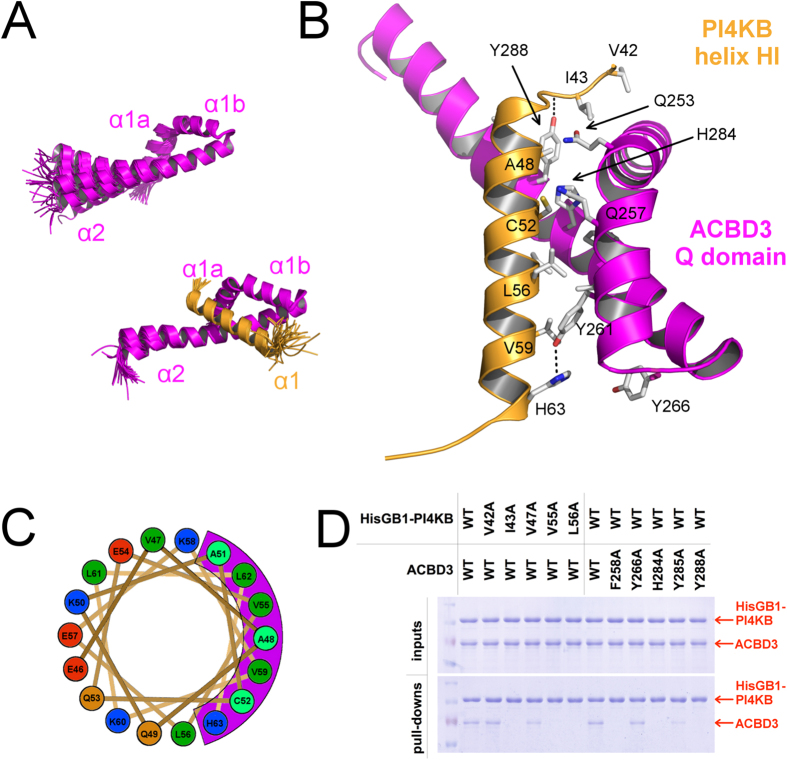
Figure 2. Structural analysis of the ACBD3:PI4KB complex.
(A) Overall structure of the ACBD3 Q domain by itself and in complex with the PI4KB N-terminal region. Superposition of the 30 converged structures obtained for the Q domain (top) and the 45 converged structures obtained for the complex (bottom), with only the folded part of PI4KB shown (see SI Fig. 2 for the complete view). (B) Detailed view of the complex. The interaction is facilitated by only two hydrogen bonds (ACBD3 Tyr261: PI4KB His63 and ACBD3 Tyr288: PI4KB Asp44), while the hydrophobic surface of the kinase helix nests in the ACBD3 Q domain. ACBD3 is shown in magenta and PI4KB in orange. (C) Top view of the kinase helix. The kinase helix is amphipathic and its hydrophobic surface overlaps with the ACBD3 binding surface (shown in magenta). Strong and weak hydrophobes are in green and cyan respectively, basic residues in blue, acidic residues in red and nonpolar hydrophilic residues in orange. (D) Pull-down assay with a NiNTA-immobilized N-terminally His6GB1-tagged PI4KB kinase and untagged ACBD3 protein. Wild type proteins and selected point mutants of both PI4KB and ACBD3 were used. Inputs and bound proteins were analyzed on SDS gels and stained with Coomassie Blue. Cropped gels ran the same experimental conditions are shown. Please, see SI Fig. 9 for original full-length gels.