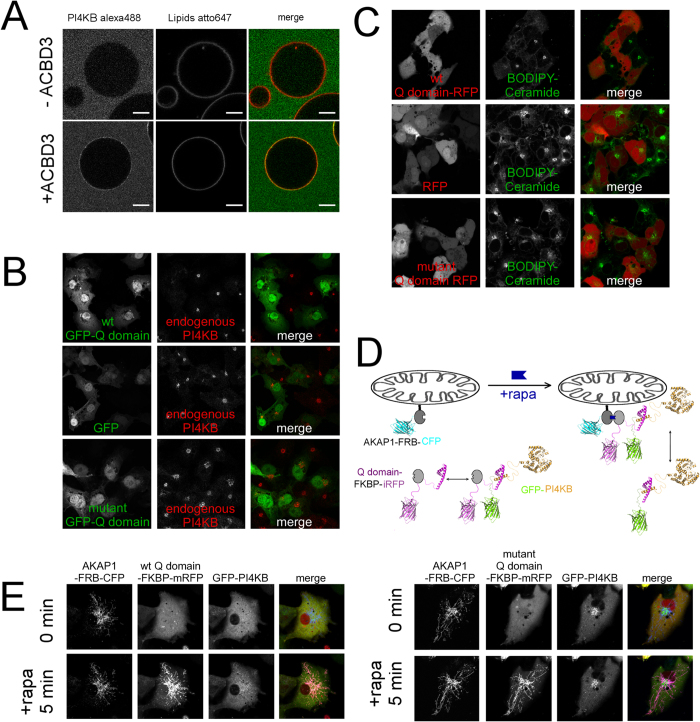
Figure 3. ACBD3 is sufficient to recruit the PI4KB kinase to membranes.
(A) GUVs recruitment assay. Top – Virtually no membrane bound kinase was observed when 600 nM PI4KB was added to the GUVs. Bottom – in the presence of 600 nM GUV tethered ACBD3 a significant signal of the kinase is detected on the surface of GUVs. (B) Golgi displacement experiment. Upper panel: ACBD3 Q domain fused to GFP was overexpressed and the endogenous PI4KB was immunostained. Middle panel: The same experiment performed with GFP alone. Lower panel: The same experiment performed with mutant Q domain (F258A, H284A, Y288A) that does not bind the PI4KB. (C) ACBD3 Q domain overexpression inhibits ceramide transport to Golgi – COS-7 cells transfected with wild-type ACBD3 Q domain-FKBP-mRFP were loaded with 0.05 μM Bodipy FL-Ceramide for 20 min, then washed and depicted after 20 min. Middle panel – The same experiment performed with mRFP-FKBP alone. Lower panel – The same experiment performed with mutant Q domain (F258A, H284A, Y288A) that does not bind the PI4KB. (D) Scheme of the mitochondria recruitment experiment. – The AKAP1-FRB-CFP construct is localized at the outer mitochondrial membrane, while the GFP-PI4KB and Q domain-FKBP-mRFP constructs are localized in the cytoplasm where they can form a complex. Upon addition of rapamycin the Q domain-FKBP-mRFP construct translocates to the mitochondria and takes GFP-PI4KB with it. (E) Mitochondria recruitment experiment. Left – cells transfected with AKAP1-FRB-CFP, GFP-PI4KB and wild-type Q domain-FKBP-mRFP constructs before and five minutes after addition of rapamycin. Right – The same experiment performed using the H264A Q domain mutant.