Figure 6. Proposed models of Hh signalling pathways used by recShh and SAG or MPHh+ and GSA-10, respectively, to inhibit adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells.
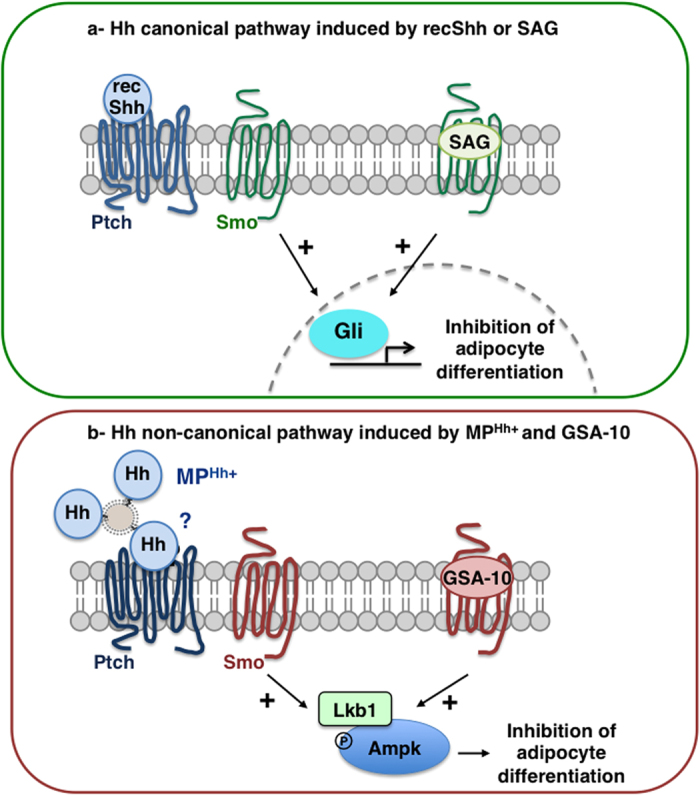
(a) Hh canonical pathway induced by recShh and SAG. Non-lipidated form of Hh (recShh) or SAG by binding to Ptch and Smo, respectively, inhibits 3T3-L1 adipogenesis in minimal induction medium through Smo activation leading to Gli factors transactivation, and adipocyte differentiation inhibition.(b) Hh non-canonical pathway induced by MPHh+ and GSA-10. MPHh+ (by binding to Ptch ?) trigger a potent inhibition of adipocyte conversion similar to the inhibitory effects of recShh or SAG, but molecular mechanisms differ and involve non-canonical Hh signalling. Smo agonist GSA-10 recapitulates the hallmarks of MPHh+-induced anti-adipogenic effects. Despite a Smo-dependency, MPHh+ and GSA-10 effects are independent of increased transcription of Gli1 factors. Conversely, MPHh+ and GSA-10 both rely on a Smo/Lkb1/Ampk axis to exert their anti-adipogenic effects, illustrating non-canonical Hh responses.
