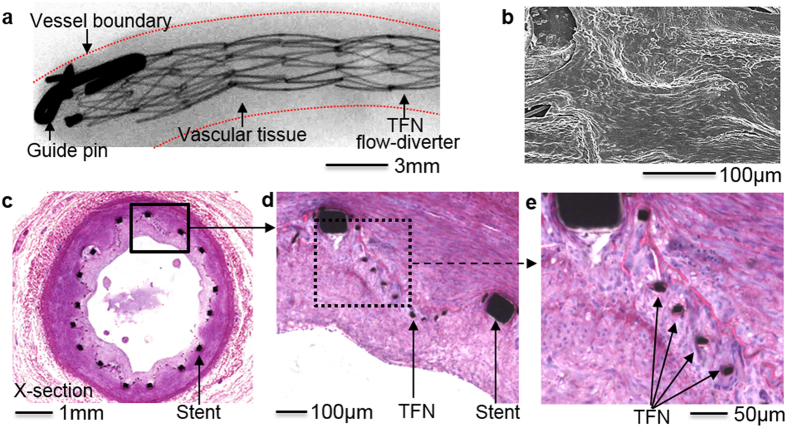
Figure 6. In vivo study of the device feasibility.
(a) Micro X-ray image (30 days follow-up) of a TFN flow-diverter deployed in the distal region of the right common carotid artery in a swine model. (b) Scanning electron microscopy image showing the device with the newly grown healthy endothelial cell layers. (c–e) Histopathology images of the flow-diverter implanted over a month. The results show nicely grown tissues on the highly porous, hyper-elastic TFN membranes without significant thrombosis formation or abnormalities.