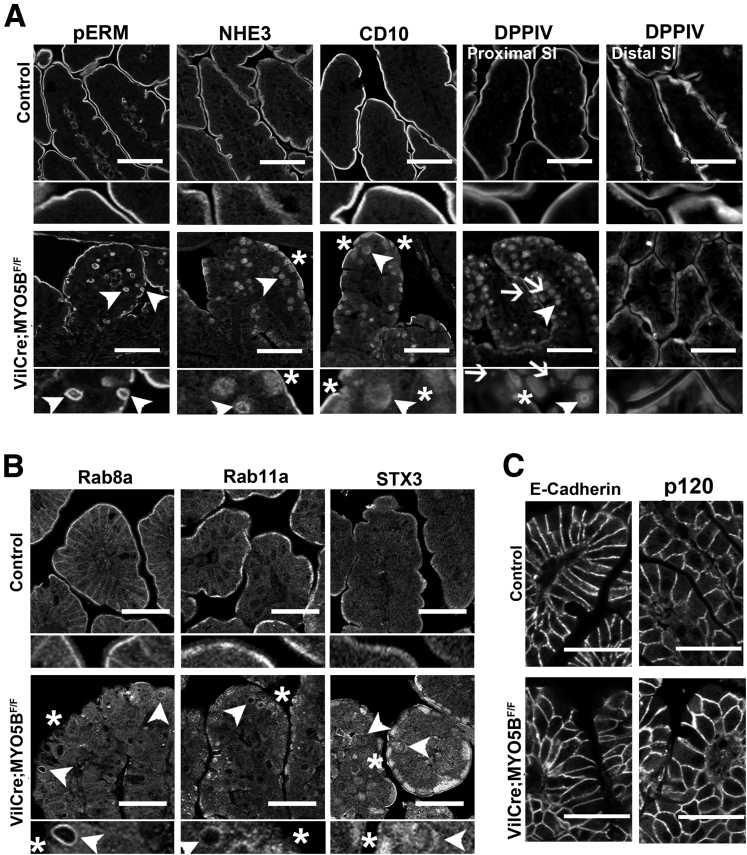
Figure 14.
Disruption of apical trafficking in VillinCre;MYO5BF/Fduodenum. (A) Control (top row) and VillinCre;MYO5BF/F (bottom row) duodenal sections were immunostained for apical proteins (pERM, NHE3, CD10, and DPPIV). pERM staining in control duodenum showed microvilli located only on the apical surface of the villi enterocytes. In VillinCre;MYO5BF/F duodenum, pERM immunostaining identified microvillus inclusions inside enterocytes as well as the formation of microvillus inclusions at the apical surface of enterocytes (arrowhead). The apical exchanger NHE3 normally was located on the apical membrane of enterocytes in the small intestine. Upon MYO5B loss, NHE3 was mislocalized to a diffuse subapical compartment (asterisk) and labeled in inclusions (arrowhead). CD10 and DPPIV both labeled the apical brush border in control mice. In VillinCre;MYO5BF/F duodenum, CD10 and DPPIV were relocated into a diffuse subapical localization (asterisk) as well as into internal inclusions (arrowheads). DPPIV also was found localized to small punctate vesicles (arrows). In VillinCre;MYO5BF/F distal small intestine (last column), although some DPPIV subapical accumulation was observed, no apparent overall difference was noted in comparison with control. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Apical trafficking proteins, Rab8a, Rab11a, and STX3, were concentrated subapically in control tissue, with Rab8a also labeling along lateral membranes. Rab8a and Rab11a were lost from the apical membrane with a small accumulation in the subapical regions (asterisk), and occasionally localized to inclusions (arrowheads) in VillinCre;MYO5BF/F duodenum. STX3 was collapsed into a diffuse subapical region (asterisk) as well as localized to inclusions (arrowheads). Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Control and VillinCre;MYO5BF/F duodenum were immunostained for E-cadherin and p120. In both controls and VillinCre;MYO5BF/F duodenum, E-cadherin and p120 labeled the basolateral membranes with no obvious differences between them. Scale bar: 50 μm. SI, small intestine.