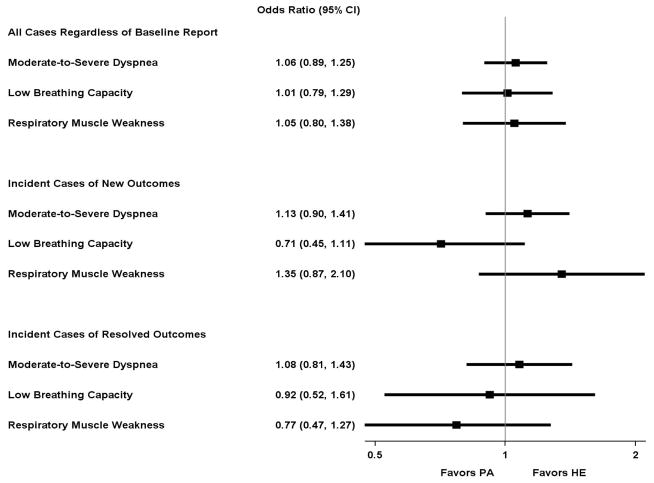
Figure 2.
Odds ratioa (95% CI) for effect of physical activity intervention on categorical respiratory outcomesb over time
CI, confidence interval; FEV1, Forced expiratory volume in 1 second; HE, health education; MIP, maximal inspiratory pressure; LLN, lower limit of normal; PA, physical activity.
aCalculated as the average odds ratio across the 30-month follow-up, adjusted for field center and gender.
bModerate-to-severe dyspnea (Borg index>2), low breathing capacity (FEV1<LLN), and respiratory muscle weakness (MIP<LLN).