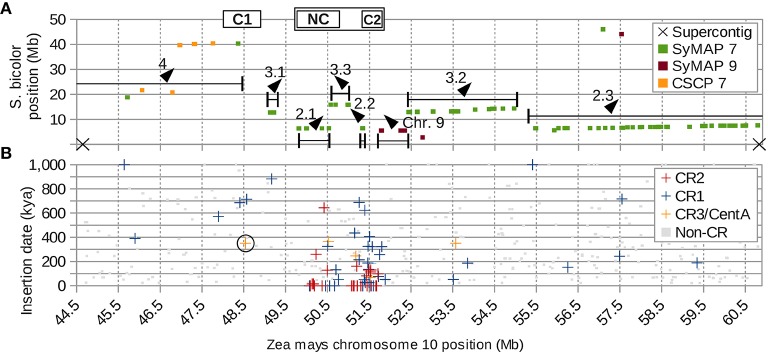
Figure 7.
Supercontig of CEN10 and hemicentric inversions. (A) Seven jumbled blocks of syntenic sorghum chromosome 7 markers (SyMAP 7) are numbered according to their positions in sorghum, with direction indicated by arrows. Boxed C1 and C2 indicate positions of the CentC clusters, NC indicates the CR cluster with no CentC (Figure 1). The cenH3 binding region CEN10 is marked by the box surrounding NC and C2. Single-copy pericentromere markers conserved between sorghum and maize (CSCP) are shown. CSCP 7 markers of sorghum chromosome 7 are near C1. Sorghum chromosome 9 markers (SyMAP 9) that originated from the end of a larger syntenic block 40 Mb away (Figure S10) were deposited near CEN10 of maize by several inversions involving centromere-proximal DSBs, which are confirmed by the presence of a CR1 element at the distant end of the SyMAP 9 block (Figure S9B). Ends of blocks do not coincide with either of the two supercontig breaks in this region of the reference genome, indicating that breaks in synteny are real and not artifacts of sequence assembly. (B) CR and non-CR elements graphed by estimated insertion time and chromosome location indicate that C1 has become inactive >300 kya. The CR element used to date the split of C1 from C2 resulting in inactivation of C1 is circled. CR3/CentA = CR3 and CentA (nonautonomous CR3).