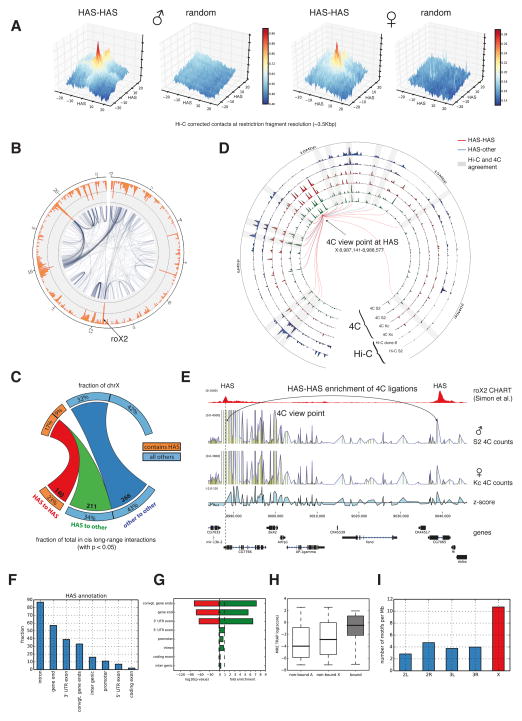
Figure 2. HAS show more Hi-C and 4C ligations with other HAS.
A. Enrichment of Hi-C contacts between HAS loci in male (S2) and female (Kc) data (see Experimental Procedures). The x- and y-axes show distance from HAS in restriction fragment resolution. The z-axis contains the mean value of all pooled normalized sub-matrices corresponding to a HAS-HAS intersection. B. Representation of long-range Hi-C contacts from S2 cells as a network (25 kb bins, p-value<0.05, see Experimental Procedures). The orange outer rim shows the total number of long-range Hi-C contacts per bin. C. Quantification of long-range interactions on chromosome X from HAS to HAS (red), HAS to other regions (green) and within other regions (dark blue). Multiple HAS found in same bins were considered once. D. Comparison of enriched 4C contacts in males and females and Hi-C contacts in two cell lines for the view point at HAS position X:8,987,141-8,988,577. Tracks displayed from outside towards the inside: Hi-C S2 and Hi-C clone-8 adjusted –log(p-values) for a 25 kb binning; 4C contact enrichment –log(p-values) for Kc replicate1, Kc replicate2, S2 replicate1 and S2 replicate2 at 25 kb binning. Lines represent enriched contacts detected in one of the 4C S2 replicates. Red lines indicate interactions between HAS and the blue line indicates interactions from HAS to other regions. Peripheral numbering indicates genomic position in Mb. Grey rectangles highlight the agreement between Hi-C and 4C at the enriched 4C contacts at the connecting lines. Close to the view point the detection of enrichments that are close to TAD size is limited when using Hi-C data. E. 4C data for a viewpoint at the end of gene CG7766 confirms the interaction between two HAS that are 50 kb apart. Further 4C examples are in Figure S5C. F. Graph representing the location of HAS on different regions in and around genes. G. Enrichment of MREs bound by the MSL complex in contrast to the genome-wide background occurrence of MREs. H. TRAP score for MREs on autosomes (non-bound A), MREs not bound by the MSL complex on chromosome X (non-bound X), and MREs bound to the MSL complex (bound). H. Occurrence of MREs at different chromosomes filtered by the following criteria: the MRE has to be on active chromatin determined using H3K36me3 (GEO accession GSM685608), the MRE has to be located near the gene end, the MRE needs to have a TRAP score of at least -2 and the MRE should be located within 25 kb of the nearest boundary. MREs on chromosome X are enriched for these features. See also Table S3 and S4 and Figure S4 and S5.