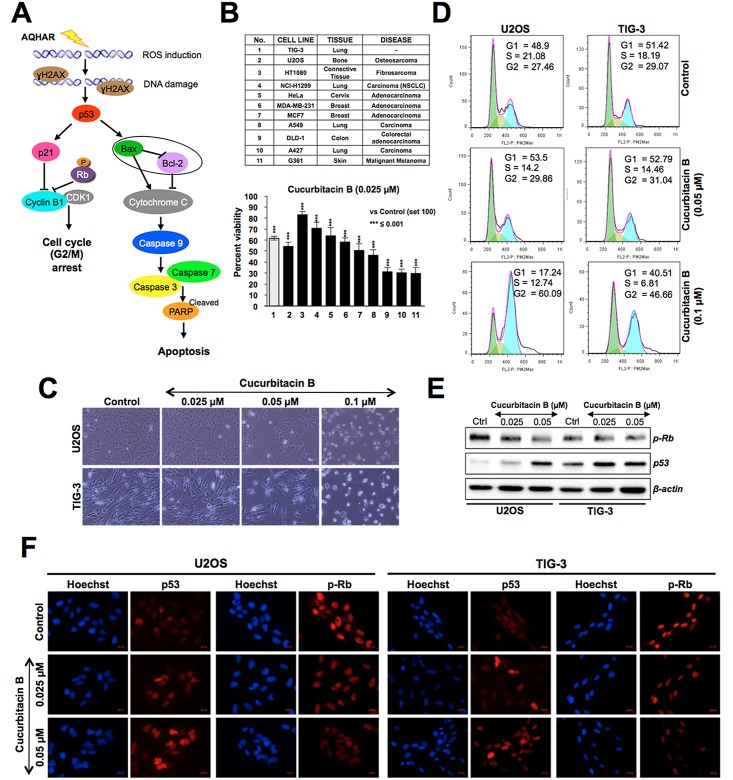
Fig 6. Cytotoxicity of curcubitacin B on cancer and normal human cells.
(A) Schematic representation showing the effect of AQHAR on cancer cells by induction of oxidative stress (ROS) and DNA-damage leading to activation of growth arrest and apoptosis signaling. (B) Effect of curcubitacin B on a variety of human cancer and normal cells, ***p<0.001 denotes statistically significant difference between the control and treated groups. (C) Phase contrast images of control and curcubitacin B-treated human osteosarcoma (U2OS) and normal (TIG-3) cells showing the toxicity to both. (D) Cell cycle analysis showing the arrest of U2OS and TIG-3 cells in G2/M phase in response to curcubitacin B treatment. (E) Cucurbitacin B-treated U2OS cells show decrease in phosphorylated RB (pRB) and increase in p53 at doses as low as 0.025 μM. Similar effects were observed by immunostaining in both cancer (U2OS) and normal (TIG-3) cells (F).