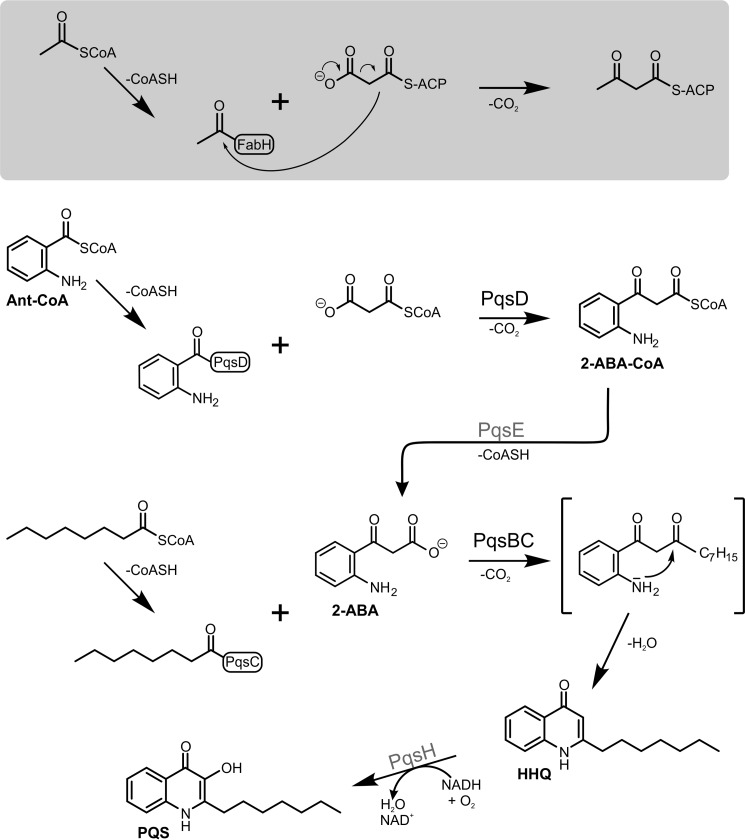
FIGURE 1.
Reactions of FabH (shaded box) and the FabH-like proteins PqsD and PqsBC involved in 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolone biosynthesis. The PqsD- and PqsBC-catalyzed reactions proceed in a similar manner to that of the model enzyme FabH. In the initial step, the acyl moiety of an activated carboxylic acid is transferred to a strictly conserved active-site cysteine residue. Subsequently, a β-ketoalkanoic acid (malonyl-ACP in case of FabH, malonyl-CoA or malonyl-ACP in PqsD, and 2-ABA in PqsBC) is decarboxylated, and the resulting reactive enolate intermediate (not shown) attacks the thioester bond of the acyl-enzyme to form the reaction product. Intermediates and products of the alkylquinolone biosynthetic pathway: Ant-CoA, anthraniloyl-coenzyme A; 2-ABA-CoA, 2-aminobenzoylacetyl-CoA; 2-ABA, 2-aminobenzoylacetate; HHQ, 2-heptyl-4(1H)-quinolone; PQS, Pseudomonas quinolone signal.