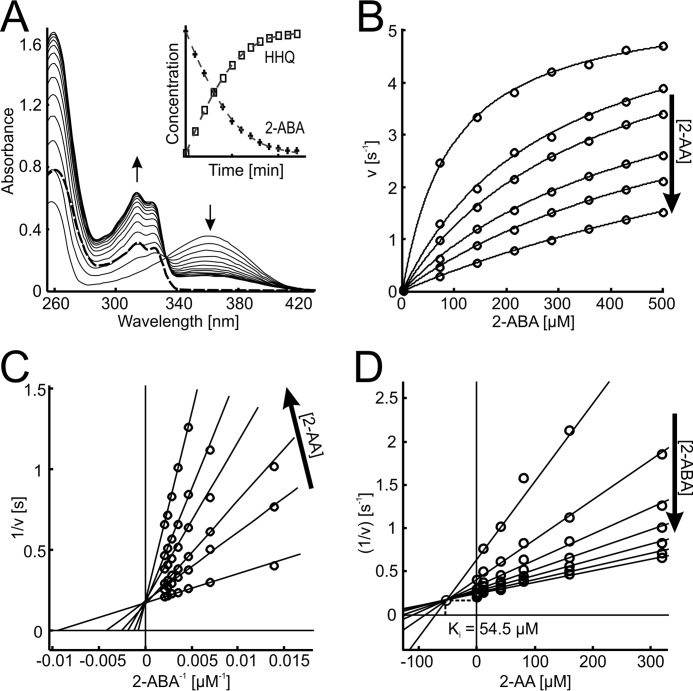
FIGURE 7.
Steady-state kinetics and competitive inhibition of PqsBC by 2-AA. A, conversion of 2-ABA (λmax at 360 nm) and octanoyl-CoA (absorbing at 260 nm) to HHQ (λmax at 313 nm). 20 nm PqsBC was mixed with 50 μm of each substrate. Spectra were measured every 60 s with a bandwidth of 1 nm. HHQ formation could be observed at 313 nm with a differential extinction coefficient of 6,520 m−1 cm−1. The remaining absorption above 340 nm after full conversion of the substrates (bold trace) is due to scattering and can be eliminated by diluting to 50% in 2-propanol/HCl (dashed trace). Inset, conversion of 10 μm substrates, monitored at 313 nm (HHQ) and 360 nm (2-ABA) with the determined extinction coefficients. Data interval is 1 min. B–D, inhibition of PqsBC activity by 2-AA. B, nonlinear fits of measured initial rates. The Lineweaver-Burk plot (C) shows the characteristic pattern of competitive inhibition. Using the Dixon plot (D), the inhibitor constant Ki of the competitive reaction could be determined graphically. Experiments were performed with 50 μm octanoyl-CoA and 20 nm PqsBC in HEPES buffer, pH 8.2, at 25 °C; arrows indicate ascending concentrations.