FIGURE 3.
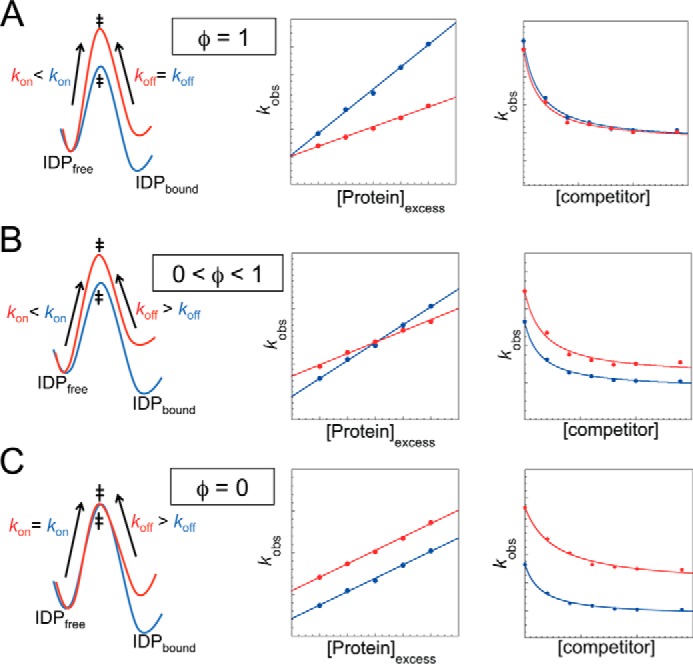
Relationship between association and dissociation rate constants and φ-values for apparent two-state systems. Shown are energy diagrams (first column), observed association rate constants under pseudo-first order conditions (middle column), and observed dissociation rate constants (third column) for wild-type IDP (blue) and mutant IDP (red). A, φ = 1, i.e. native interactions are formed in the transition state. kon is lower, and koff is unchanged. B, 0 < φ <1 structure is partially formed, resulting in changes in both kon and koff. C, φ = 0, residue is as unstructured at the transition state as in the unbound state. kon is unchanged, and koff is increased. The rate constants kon and koff are controlled by energy barrier sizes (first column), and are determined from straight-line gradients in association mixing experiments (second column) and from high concentration asymptotes in out-competition dissociation mixing experiments (third column), respectively.
