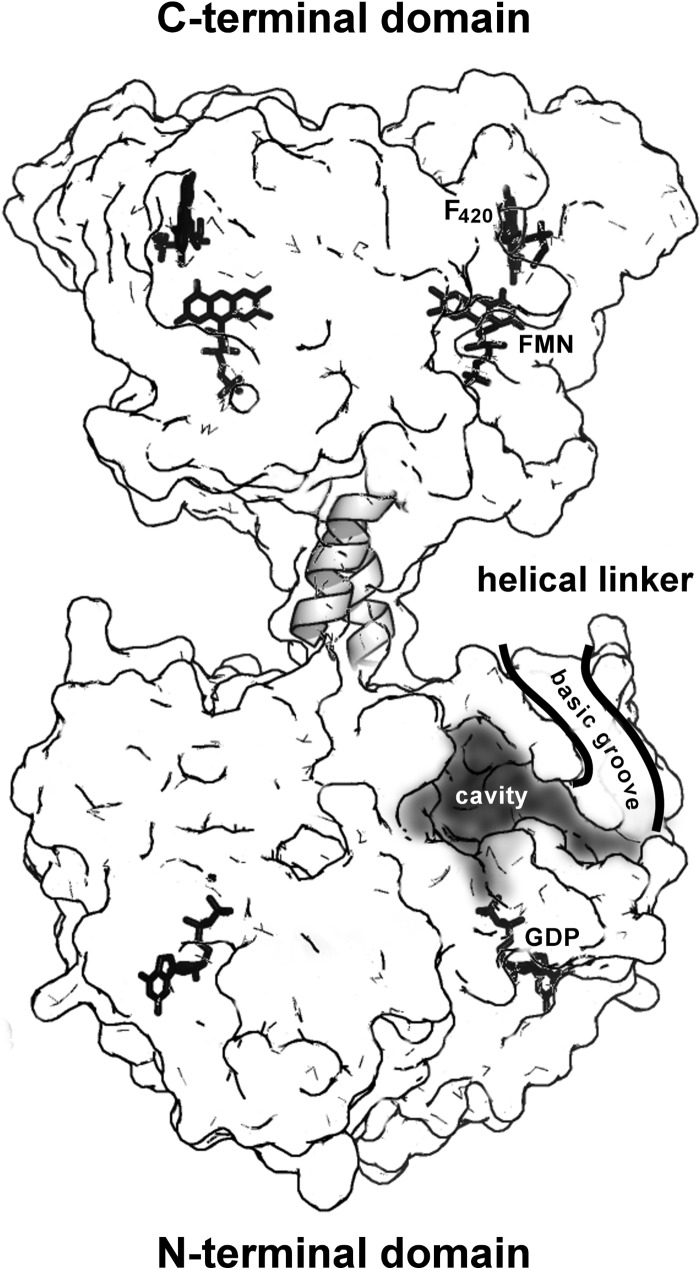
FIGURE 7.
Functional implications of a full-length structural model of FbiB. A surface representation of the “straight” model of full-length FbiB showing the separation of N- and C-terminal domains and a postulated α-helical linker. Both domains are dimeric and thus have mirrored features in the diagram, including confirmed locations of FMN and F420 in the C-terminal domain and GDP in the N-terminal domain (by comparison with the homolog CofE structure) as well as a postulated binding cavity for F420 and l-glutamate in the N-terminal domain. The surface is partially transparent, and ligand binding or active sites indicated on the left are located in the back of the model, whereas those on the right are on the front of the model. We hypothesize that electrostatically positive surface grooves (basic grooves) lined with numerous arginine and lysine side chains have a role in binding an elongated and negatively charged F420 poly-γ-glutamate tail and directing it toward solvent space (only the front groove is shown for clarity).