FIGURE 4.
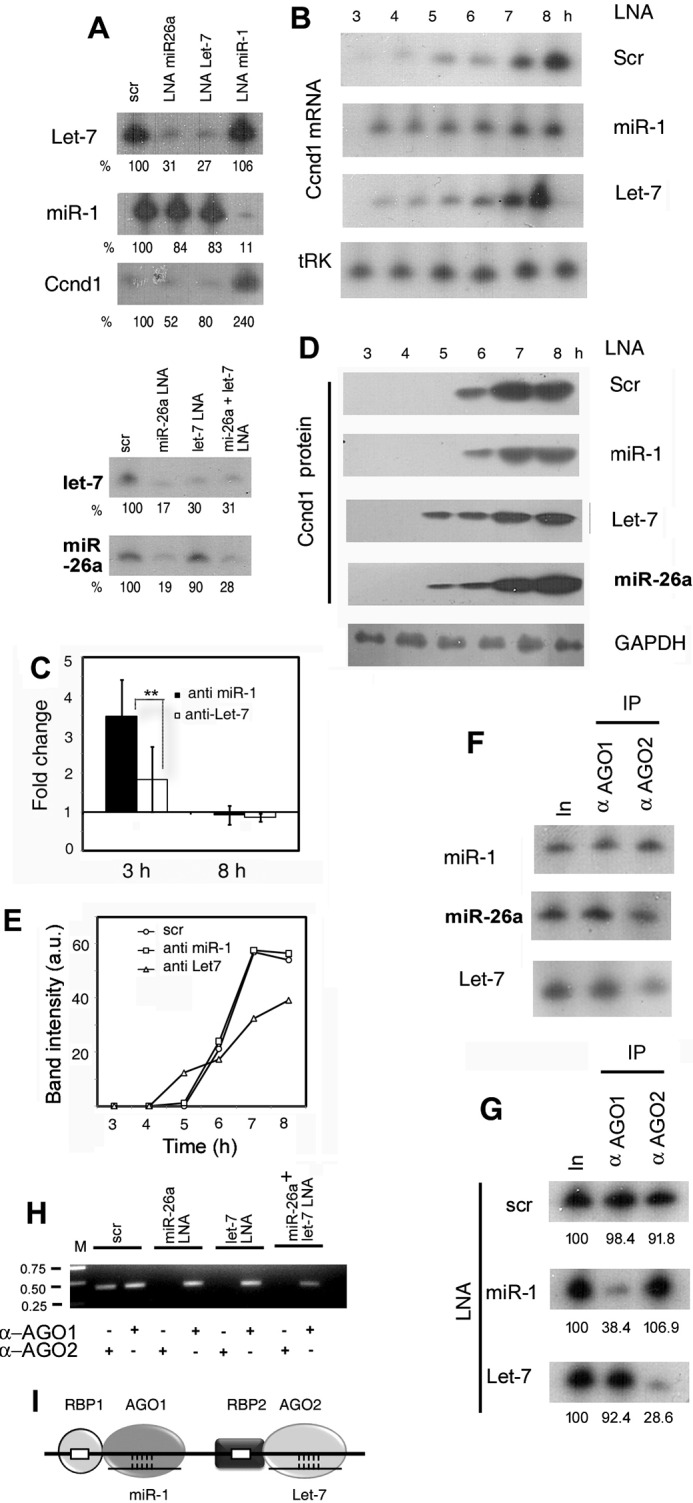
Effect of antagomirs on Ccnd1 expression and AGO-mRNA association. A, specificity and efficiency of antagomir action. Northern blots of 4-h serum stimulated L6 cells treated with LNAs of scrambled-sequence (scr), or targeted against the indicated miR, probed with the specified antisense oligonucleotide. The top and bottom panels are from two independent experiments. B, time course of Ccnd1 RNA in cells treated with control or targeted antagomirs. C, fold change of Ccnd1 mRNA in targeted LNA-treated versus scrambled LNA-treated cells at 3 and 8 h post-serum addition. D and E, time course of Ccnd1 protein expression of LNA-treated cells. The loading control (tRNALys or tRK) for AGO2 siRNA-treated cells is shown at the bottom. F, binding of AGO isoforms to miRs. Immunoprecipitates of AGO1 or AGO2 were probed for indicated miRs by Northern blot. G and H, effect of LNA treatment on AGO-mRNA binding. R-CLIP assay of extracts of L6 cells transfected with indicated LNA antagomirs and serum stimulated for 4 h, using anti-AGO1 or anti-AGO2 antibody. The two panels show independent experiments. In, input RNA. G, Northern blot probed for Ccnd1; (H) RT PCR using Ccnd1 primers. I, postulated role of RBP in positioning of miR-AGO complexes on mRNA. The AGO isoforms interact with distinct RBPs, which have binding sites on the mRNA in close proximity to the miR target site.
