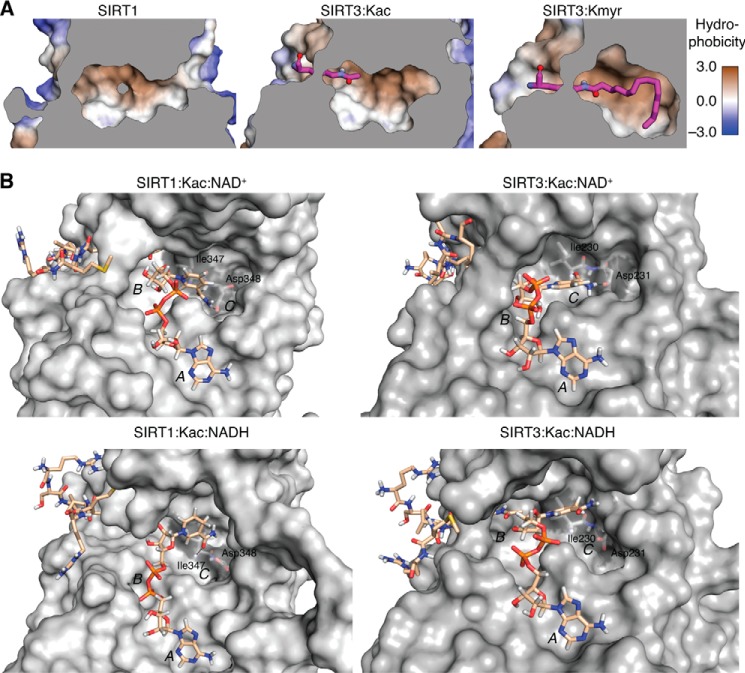
FIGURE 7.
Molecular modeling structures. A, the SIRT1 and SIRT3 active sites were analyzed for their hydrophobicity to determine the potential for binding long-chain fatty acyl groups. Structures shown are crystal structures of SIRT1 (Protein Data Bank entry 4KXQ) and model structures for active site complexes of SIRT3·Kac and SIRT3·ϵ-N-myristoyllysine (Kmyr) (modified from 3GLR). Conformations shown are the most energetically favorable. Gray areas indicate the position of a slice through the vertical z-plane. B, Conformations obtained after the production run of SIRT1 and SIRT3 in complex with ϵ-N-acetylated peptide substrate and NAD+ or NADH. Substrates are shown with carbon atoms in beige, and non-polar hydrogen atoms have been omitted from the peptide substrate. Isoleucine and aspartate residues forming hydrogen bonds with NAD+ and A, B, and C pockets for NAD+ binding have been labeled.