Figure 2.
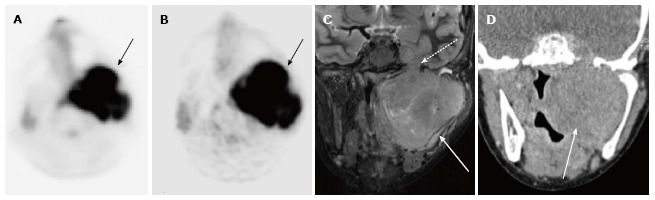
12-year-old male with rhabdomyosarcoma. Axial PET image from PET-MRI (A) shows intense FDG uptake in the left parapharyngeal region (black arrow). Axial PET image from PET-CT (B) shows similar uptake in the same region (black arrow). Coronal T2-weighted fat suppressed image from the MRI portion of the examination (C) clearly shows extent of tumor (white arrow) including perineural spread through foramen rotundum (white dashed arrow). Tumor is not as well delineated on this coronal CT image from the PET-CT examination (D) (white arrow). PET-MRI: Positron emission tomography-magnetic resonance imaging; CT: Computed tomography; FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose.
