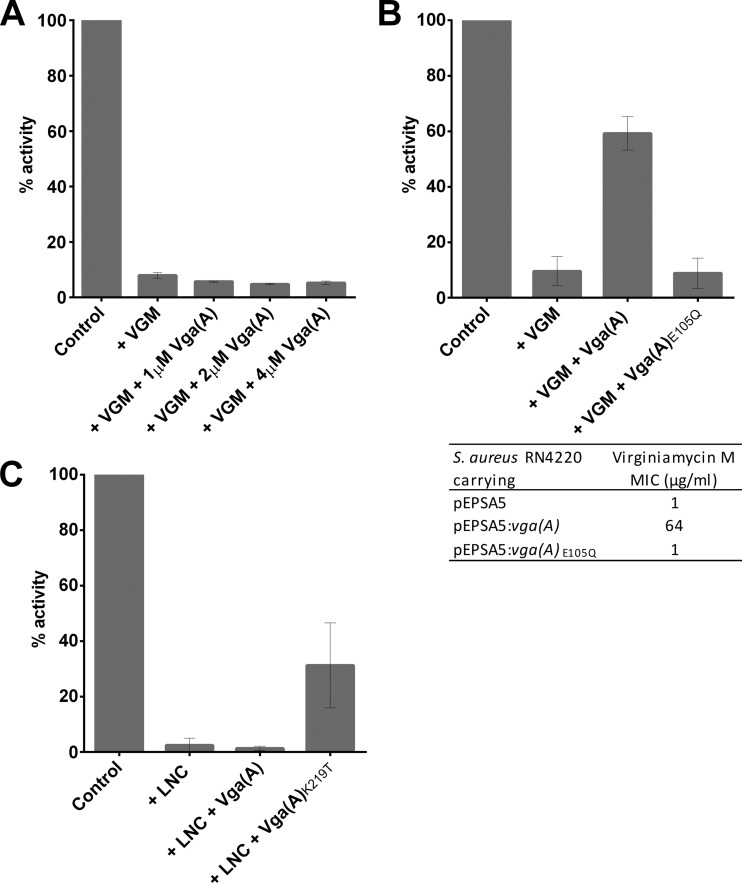
FIG 4 .
Recapitulation of resistance phenotypes associated with ARE ABC-F proteins in vitro. (A) When expressed in E. coli, Vga(A) does not confer resistance to virginiamycin M (21); addition of Vga(A) to an E. coli T/T assay containing ≥IC90 of virginiamycin M (VGM) also failed to restore translational activity. (B) ATPase activity is essential for Vga(A) function (21), and abrogation of ATPase activity of the N-terminal ABC domain rendered Vga(A) inactive when expressed in S. aureus RN4220; the purified ATPase-deficient Vga(A)E105Q protein also failed to protect staphylococcal translation from inhibition by virginiamycin M in vitro. (C) A single-amino-acid substitution in the interdomain linker expands the resistance spectrum of Vga(A) to encompass lincomycin (20). Addition of the purified Vga(A)K219T to a staphylococcal T/T assay inhibited with a >IC90 of lincomycin (LNC) restored translational activity, while addition of the wild-type protein did not. Results are means from at least three independent determinations, and error bars show standard deviations.