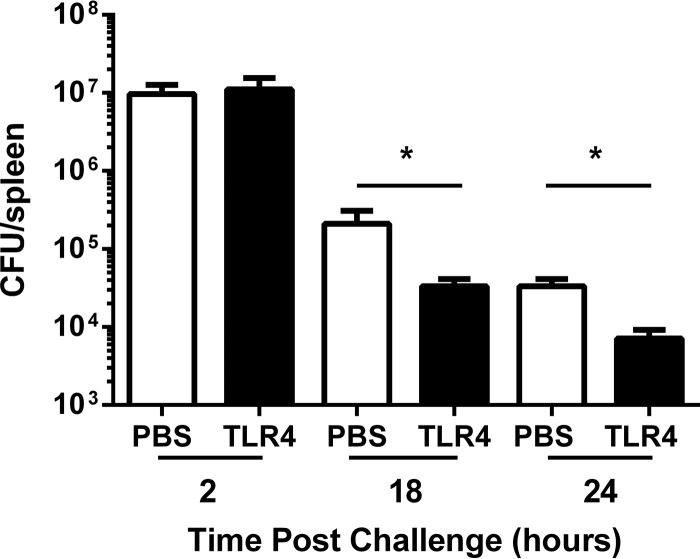
FIG 3.
TLR4 stimulation prior to S. epidermidis challenge reduced splenic bacterial burden at 18 and 24 h postchallenge relative to the results seen with PBS-treated control animals. Three days prior to bacterial challenge, groups of 5 immunocompetent BALB/c WT mice were s.c. injected with 200 μl of PBS or a TLR4 agonist (E6020). Mice were challenged i.v. with 1.8 × 108 CFU (2 and 24 h) or 6.56 × 108 CFU (18 h) of biofilm-grown S. epidermidis. The splenic bacterial burden at 2, 18, or 24 h postchallenge is shown. Bars represent the mean bacterial burden for the group, and error bars represent standard deviations. *, statistically significant difference in splenic bacterial burden between PBS-treated and TLR4 agonist-treated mice at 18 h (P = 0.0079 [Mann-Whitney]) and 24 h (P = 0.0079 [Mann-Whitney]) postchallenge.