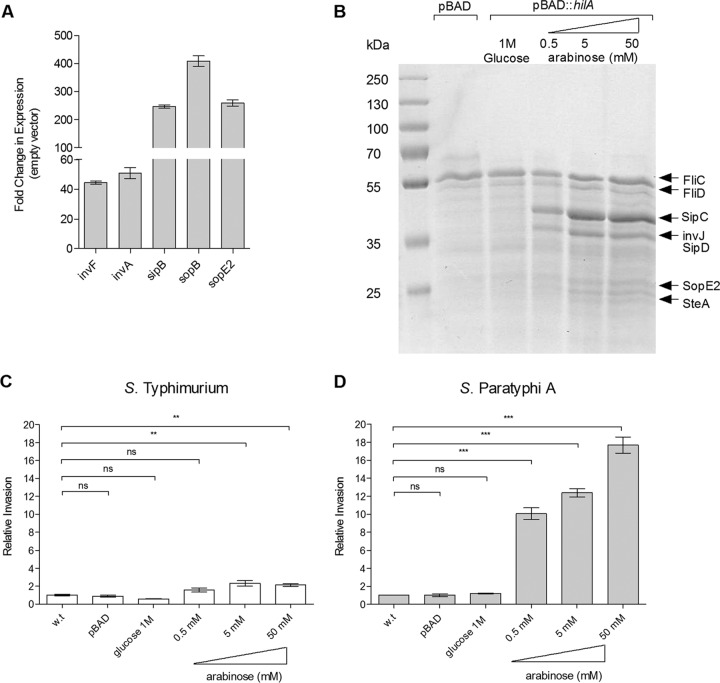
FIG 5.
Induced expression of SPI-1 increases S. Paratyphi A invasion. (A) Total RNA was harvested from S. Paratyphi A 45157 carrying pBAD18 or pBAD::hilA grown in LB supplemented with 100 μl/ml ampicillin and 50 mM arabinose to late logarithmic phase aerobically and was subjected to qRT-PCR. The fold change in the abundance of SPI-1 gene transcripts (normalized to rpoD) in S. Paratyphi A harboring pBAD::hilA is shown relative to their expression in S. Paratyphi A carrying pBAD18. The indicated values present the means and the SEM from three independent RT-PCR experiments from two independent RNA extractions. (B) S. Paratyphi A cultures were grown aerobically in LB to logarithmic phase and normalized to an OD600 of 1.2. Secreted fractions from S. Paratyphi A carrying pBAD18 (lane 2) or pBAD::hilA grown in the presence of 1 M glucose (lane 3) or increasing arabinose concentrations (lanes 4 to 6) were separated on SDS-12% polyacrylamide gels and stained with Coomassie G-250. (C) S. Typhimurium SL1344 (wild type) and its isogenic strains carrying pBAD or pBAD::hilA were grown in LB, LB supplemented with 1 M glucose, or LB with increasing concentrations of arabinose under aerobic conditions and used to infect HeLa cells. Invasion is shown relative to that of the wild-type strain (grown in LB supplemented with 50 mM arabinose), presenting a 3.7% ± 0.76% invasion rate (from the infecting inoculum) under these conditions. (D) S. Paratyphi A 45157 and its isogenic strains carrying pBAD or pBAD::hilA were grown and used to infect HeLa cells as described for panel C. Invasion is shown relative to that of the S. Paratyphi A wild-type strain, presenting, on average, 0.05% ± 0.001% invasion. ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparison test was implemented to compare the invasion of the different strains to that of the wild type. The results represent the means and SEM from at least three biological replicates. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.