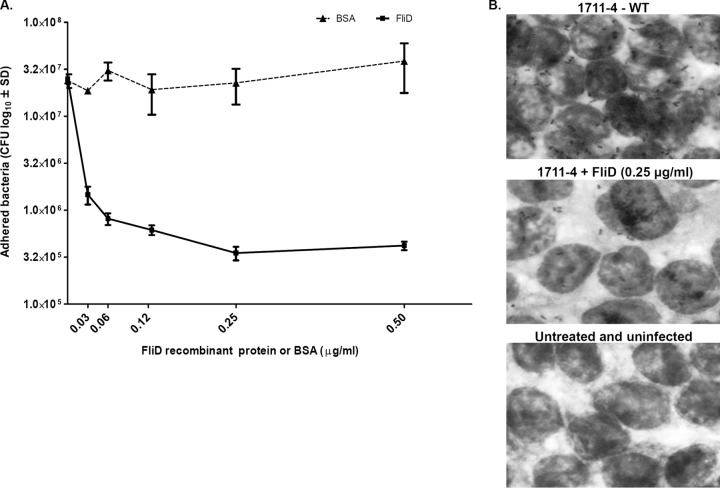
FIG 3.
Recombinant FliD inhibits adherence of aEPEC strain 1711-4 to differentiated Caco-2 cells. (A) Quantitative plate assays were performed with different FliD or BSA concentrations. Note the binding saturation obtained with FliD at 0.25 μg/ml. The number of CFU detected in cell monolayers treated with 0.5 μg/ml (4.1 × 105 CFU) was similar to that observed with 0.25 μg/ml (3.5 × 105 CFU). The presence of BSA did not interfere with bacterial cell adherence. Error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). Values were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Light microscopy of Caco-2 monolayers pretreated with recombinant FliD or left untreated. Note the significant reduction in the adherence of bacteria to Caco-2 cells pretreated with FliD at 0.25 μg/ml. Packed bacterial clusters adhering to the cells were observed on cell monolayers not treated with FliD, in contrast to the few bacteria present on monolayers pretreated with FliD and infected with 1711-4. WT, wild type.