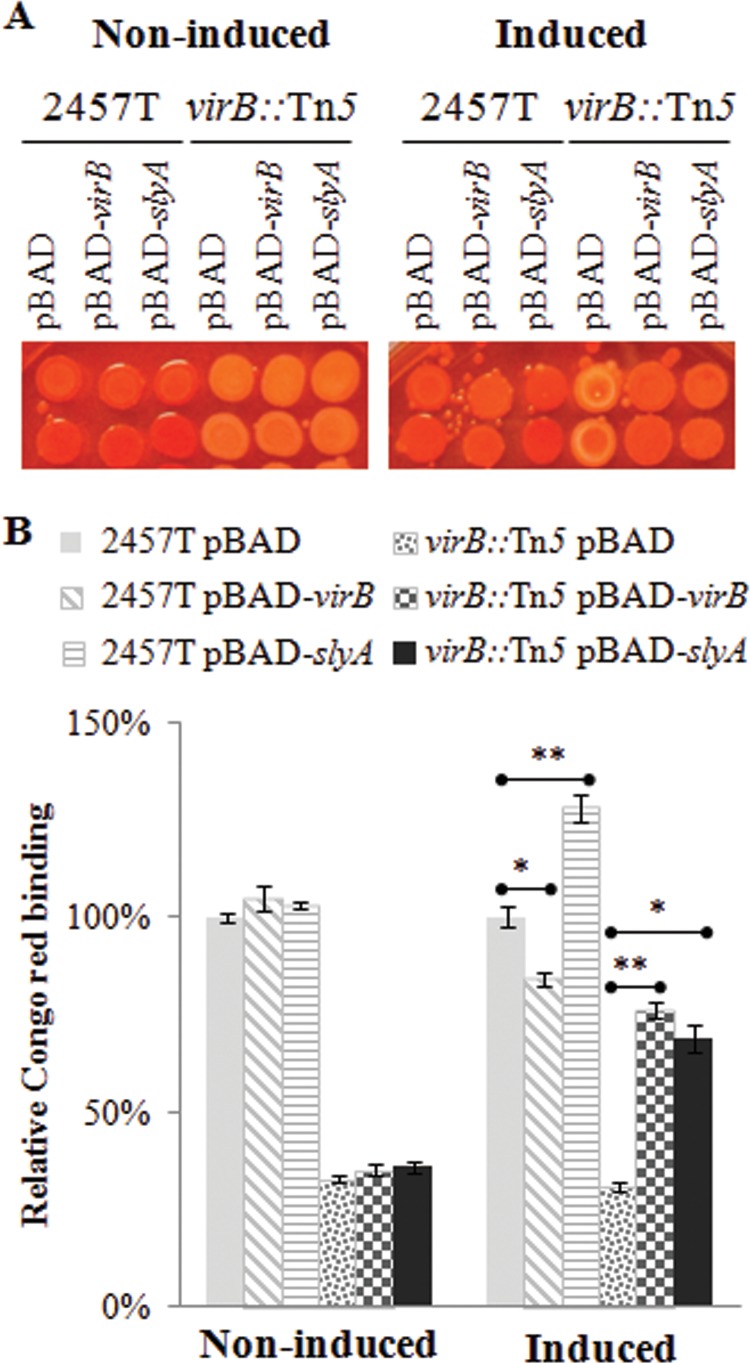
FIG 4.
Exogenous expression of slyA rescues the Congo red binding deficiency in a virB mutant. (A) Qualitative analysis of Congo red binding. S. flexneri 2457T wild-type and virB::Tn5 strains harboring pBAD, pBAD-virB, or pBAD-slyA were serially diluted (40-fold dilutions) and spotted (approximately 6 μl) onto TSA Congo red plates supplemented with 0.2% (wt/vol) d-glucose (noninduced) or 0.2% (wt/vol) l-arabinose (induced). (B) Quantitative analysis of Congo red binding. Two culture spots (shown in panel A) were scraped off the agar plate and resuspended in 0.75 ml 25% ethanol to remove the Congo red bound to cells. The OD600 was determined to normalize samples against cell number. Cell suspensions were centrifuged to pellet cells, and the OD498 of the supernatant was determined. Relative Congo red binding was calculated as [(OD498/OD600)/(average (OD498/OD600)2457T pBAD)] × 100. Data shown are representative of three independent trials. A two-tailed Student's t test (assuming equal variance) was used for statistical analysis. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001.