Figure 4. YAP Regulates the Human Naive State and Acts in Part by Modulating Wnt Signaling.
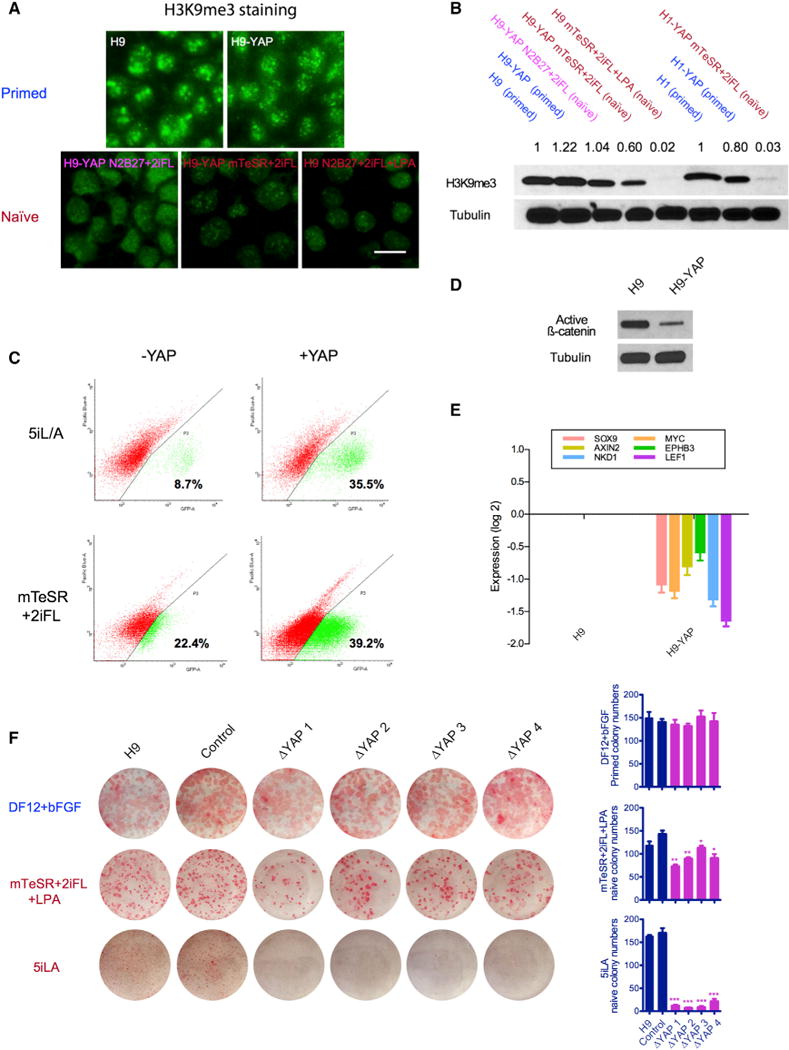
(A) H3K9me3 is strongly reduced in naive H9 ESCs, as seen by immunofluorescence. Upper panel: H9 and H9-YAP in DF12+bFGF primed medium. Lower panel: H9-YAP in N2B27+2iFL naive medium, H9-YAP in mTeSR+2iFL naive medium, and H9 in mTeSR+2iFL+LPA naive medium. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(B) Decreased total amount of H3K9me3 in Yin-PSCs and Lin-PSCs was confirmed by western blotting. Tubulin was used as loading control. Values indicate densitometry analysis of the H3K9me3 level normalized to tubulin.
(C) Flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of OCT4-ΔPE-GFP+ WIBR3 cells with or without YAP overexpression in 5i/L/A (upper panels) or mTeSR+2iFL (lower panels) media. Cells were expanded in bulk and analyzed at passage 3, in the absence of colony picking. YAP overexpression increases the ratio of OCT4-ΔPE-GFP + cells in both media.
(D) YAP overexpression decreases levels of unphosphorylated (active) β-catenin, as shown by western blotting. Tubulin was used as loading control.
(E) YAP overexpression decreases the expression of Wnt target genes, as shown by qRT-PCR. Values were normalized to GAPDH and UBB and then compared to H9. Data are averages of triplicate PCR reactions, and error bars represent SD.
(F) YAP knockout impairs the ability of ESCs to form naive colonies. H9 controls and four clones of CRISPR/Cas9-generated YAP−/− cells cultured in DF12+bFGF (primed), mTeSR+2iFL+LPA (naive), and 5i/L/A (naive, Theunissen et al., 2014) were trypsinized to single cells, counted, and plated onto MEFs in the presence of ROCK inhibitor. Seven days later, AP staining was performed and colony numbers were counted. Error bars represent SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
