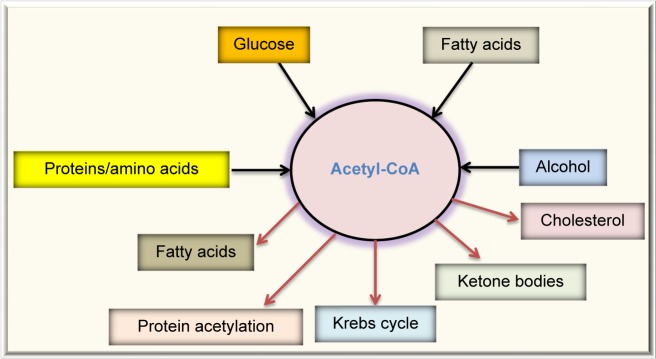
Figure 4.
Fates of acetyl-CoA, a central molecule in fuel metabolism. Acetyl-CoA can be derived by combustion of glucose, fatty acids, proteins or amino acids, and alcohol. In normal condition, acetyl-CoA is mainly channeled into the Krebs cycle for energy production. In overnutrition state, acetyl-CoA can be used to store excess energy by forming fatty acids. Acetyl-CoA is also the source for cholesterol synthesis. In starved state, acetyl-CoA is converted into ketone bodies. Acetyl-CoA is also the substrate used for protein acetylation.