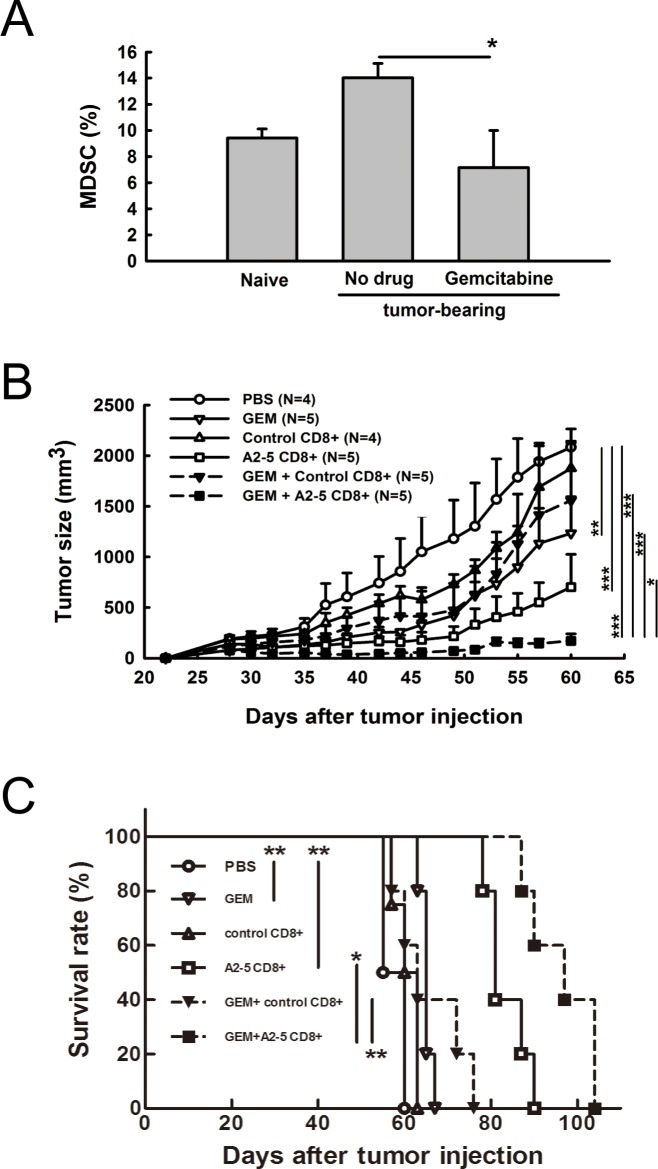
Figure 5. Combination of gemcitabine and peptide A2-5 induced CD8+ T cells provides anti-tumor activity and prolongs animal survival time in a human lung tumor xenograft model.
A. Lung cancer H2981 cells (1 × 108) were subcutaneously injected into SCID mice. Gemcitabine was i.p. injected (3mg/mouse) into mice when tumors reach ∼ 100 mm3. At day 5 after gemcitabine injection, splenocytes from tumor xenografted SCID mice were isolated and the frequency of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) was determined by using PE-conjugated anti-GR-1 antibody and FITC-conjugated anti-CD11b antibody. Error bars, SD. *P < 0.05. B. Tumor size was measured at 2–3 day intervals in each group of mice. Gemcitabine was i.p. injected (3mg/mouse) on day 25 post tumor inoculation. Peptide A2-5 induced CD8+ T cells (1 × 107) from HLA-A2 Tg mice were adoptively transferred into human tumor xenograft mice on day 30. C. Survival rate of mice determined with different treatments as shown in (B) Median survival time and log-rank test in SPSS analysis were analyzed.