Figure 4. Effects of POSTN on proliferation, anchorage independent growth, and invasion of CRC cells and its contributing signaling pathways.
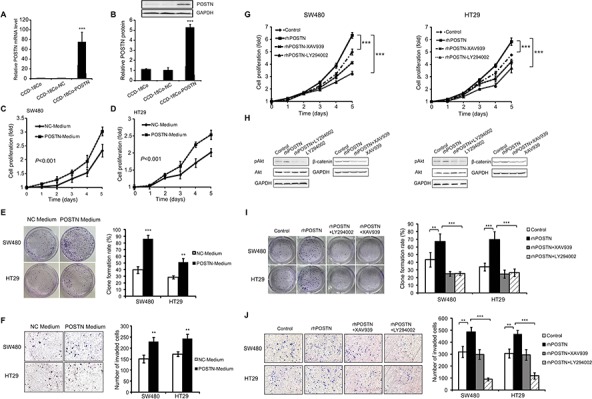
A. POSTN mRNA levels in CCD-18Co-POSTN, CCD-18Co-NC, and CCD-18Co cells. B. POSTN protein levels in CCD-18Co-POSTN, CCD-18Co-NC, and CCD-18Co cells. C. proliferation of SW480 cells in CCD-18Co-POSTN medium. D. proliferation of HT29 cells in CCD-18Co-POSTN medium. E. anchorage independent growth of CRC cells in CCD-18Co-POSTN medium. F. invasion of CRC cells in CCD-18Co-POSTN medium. G. proliferation of CRC cells treated with 100 ng/mL rhPOSTN, rhPOSTN plus 10 μM PI3K/Akt kinase inhibitor LY294002, and rhPOSTN plus 10 μM β-catenin-specific inhibitor XAV939. H. expression levels of pAkt and β-catenin in CRC cells treated with POSTN and/or signaling inhibitors by Western blot analyses. I. anchorage independent growth of CRC cells treated with POSTN and/or signaling inhibitors. J. invasion of CRC cells treated with POSTN and/or signaling inhibitors. Abbreviations and marks: CRC, colorectal carcinoma; pAkt, phosphorylation of Akt; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.
