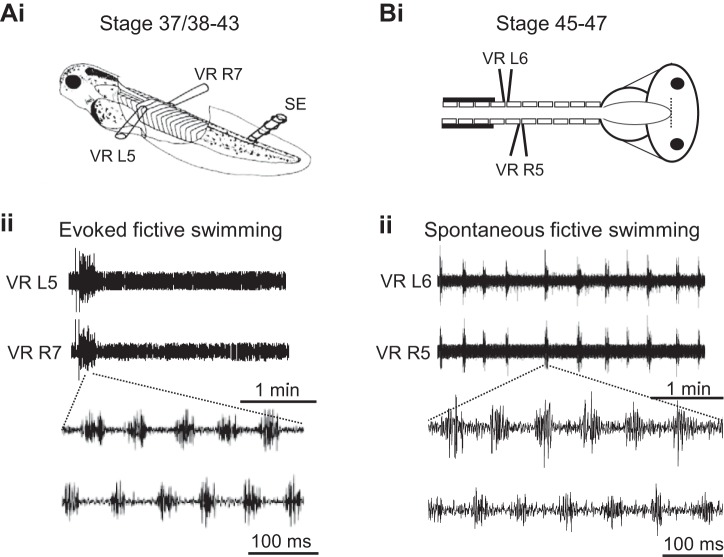
Fig. 2.
Comparison of fictive swimming in Xenopus tadpoles at stages before and after onset of free feeding. Ai: preparation used at stages 37/38–44; schematic shows a stage 42 animal immobilized in α-bungarotoxin with locations of extracellular ventral root (VR) recording electrodes on left (L) and right (R) sides and a tail-skin stimulating electrode (SE). Aii: a single episode of fictive swimming evoked by a 1-ms electrical current pulse applied via the SE. Note that, after the end of the swim bout, the preparation remains silent in the absence of further stimulation. Below is an expanded excerpt during swimming activity highlighting L/R alternation of VR bursts. Bi: equivalent preparation at stage 45–47. Bii: in the absence of any extrinsic stimulation, the preparation spontaneously generates regular episodes of fictive swimming, here, every ∼20 s. Below is an expanded excerpt of swimming activity during the indicated episode again showing L/R VR burst alternation.