FIG 1.
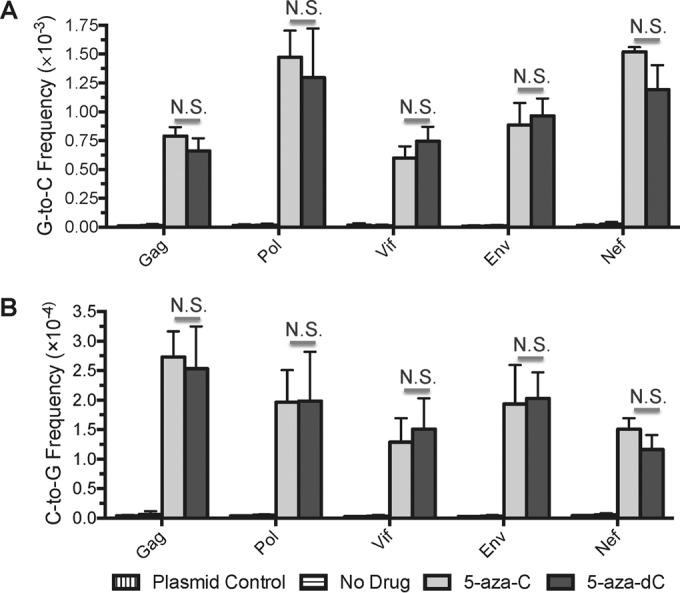
5-Azacytidine and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine induce similar levels of G-to-C and C-to-G transversion mutations during HIV-1 replication. In order to determine whether 5-azacytidine (5-aza-C) and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-aza-dC) induce similar changes in HIV-1 mutation frequencies and spectra, U373-MAGI cells were treated with DMSO (no-drug control), 5-aza-C, or 5-aza-dC. 5-Aza-C and 5-aza-dC were added 2 h before infection at the EC75 (∼260 or 3.8 μM, respectively). Cells were infected at an MOI of 1.0 with NL4-3 MIG-VSVG and were collected 72 h postinfection for the purification of genomic DNA. PCR was performed to prepare multiple amplicons (Gag, Pol, Vif, Env, Nef) from proviral DNA; these were then pooled, used to prepare libraries, and analyzed by 2 × 250 paired-end sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq system. Plasmid control amplifications were performed to determine the levels of background errors resulting from PCR and sequencing. Mutation frequencies for each amplicon, expressed as the number of mutations per base pair, were calculated by dividing the number of mutations by the number of reference bases (mutations + wild-type bases). Data represent means ± standard deviations for three independent biological replicates; N.S., not significant (P > 0.05).
