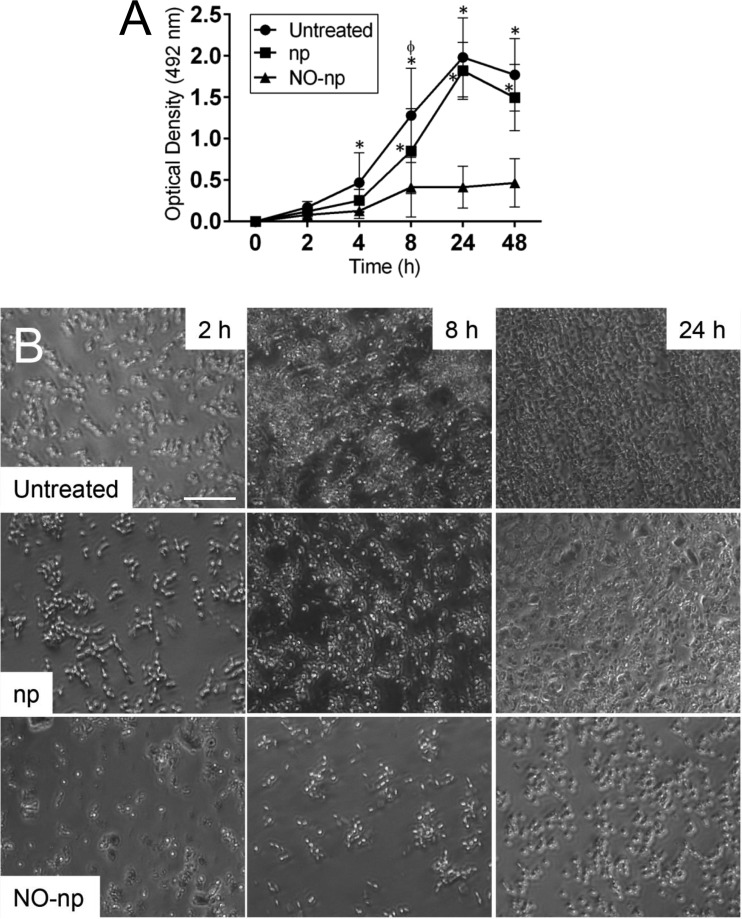
FIG 1.
NO-np inhibit biofilm formation by Candida albicans clinical isolates. (A) Kinetics of C. albicans biofilm formation in polystyrene microtiter plates grown in the absence (untreated) and presence of 5 mg/ml of nanoparticles alone (np) or nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles (NO-np), as determined by the XTT reduction assay. Each symbol represents the average value (n = 11 strains per time point), and error bars indicate standard deviations (SDs). P value significance (P < 0.05) was calculated by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and adjusted by use of the Bonferroni correction. * and ϕ, significantly higher optical densities (OD) than for NO-np and np groups, respectively. (B) Representative light microscopy images of untreated, np-treated, or NO-np-treated C. albicans SC5314 strain biofilms grown on microtiter plates for 2, 8, and 24 h. The pictures were taken at a magnification of ×20. Scale bar, 10 μm. All experiments were performed twice, with similar results obtained each time.